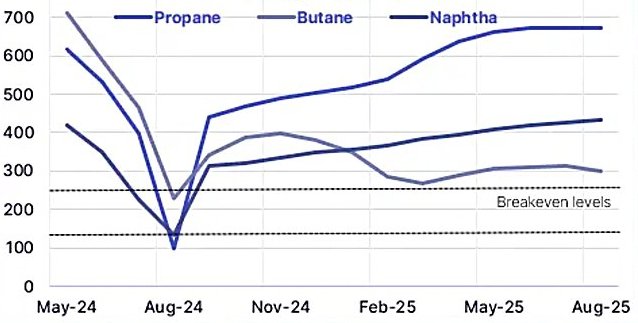
Europe’s war against plastic waste was supposed to be won by recycling. Governments poured billions into subsidizing recycling plants, imposed plastic taxes on virgin materials, and wrote regulations mandating ever-higher recycling rates and minimum recycled content. For a time, heroic promises flourished: a circular economy, hundreds of thousands of “green jobs,” and global leadership in sustainability. But now, across the continent, what’s unfolding is a stunning retreat—one that exposes a sobering truth about the policy-driven recycling revolution: market reality bites back.
The Collapse: Project Cancellations, Bankruptcies, Shuttered Plants
Far from steady progress, the past three years have delivered a torrent of closures, bankruptcies, and shelved investments. Major recycling operations—both mechanical and chemical—are pulling the plug, often after only a few years, and sometimes even before producing their first tonne of recycled product.
A Continent-Wide Wave
-
Aug 2025 -- Dow terminated its 120,000-tonne Böhlen chemical recycling project with Mura Technology in Germany, just before breaking ground, part of a wider retreat that includes shutting other assets in Europe.
-
Aug 2025 -- Veolia closed its last German recycling sites, Bernburg’s Multipet and Multiport, ending 70,000 tonnes of annual output.
-
Aug 2025 -- Biffa Limited shuttered its Sunderland, UK PET recycling plant (nearly 50,000 tonnes annual capacity) just two years after opening, citing unsustainable economics and regulatory pressure.
-
Aug 2025 -- Saperatec entered insolvency after less than a year’s operation of its composite flexible packaging delamination process plant (18,000 tonnes input capacity).
-
July 2025 -- Borealis cancelled its Schwechat mechanical recycling project in Austria, shelving a planned 60,000 tonnes per year project.
-
Jun 2025 -- Eastman polyester molecular recycling project based on Eastman PRT in the Port-Jérôme industrial zone in Normandy, France (110,000 tonnes, expandable to over 200,000 tonnes), is currently on hold as the company monitors evolving EU plastic waste regulations and faces a critical challenge due to the absence of a plan to supply electrical power to the plant before 2028, putting its timely realization in serious jeopardy.
-
Jul 2025 -- Fuenix Ecogy, supported by Sulzer and heralded as a breakthrough in chemical recycling, declared bankruptcy in the Netherlands.
-
Jul 2025 -- Neste & Ravago aborted a flagship chemical recycling plant (55,000 tonnes) in Vlissingen.
-
Feb 2025 -- Re-Match Netherlands, whose primary activity was sorting materials for recycling, went bankrupt (Tiel), despite a €4.5 million government subsidy. The Dutch factory was intended to serve as a template for 23 additional factories across Europe and North America.
-
Feb 2025 -- Carbios, a French biotech company, has announced a dramatic restructuring plan, cutting approximately 40% of its workforce amid mounting operational losses that reached €33.1 million in 2024, compared to €27.2 million the previous year. The company struggled with delays in securing financing for its flagship enzymatic-catalyzed PET depolymerization plant in Longlaville (50,000 tonnes of prepared PET waste input).
-
Jan 2025 -- Blue Cycle, Netherlands’ pioneering plastic-to-oil recycler established in late 2022, filed for bankruptcy, never reaching commercial scale (20,000 tonnes of plastic waste input).
-
2024 -- Stiphout Plastics, Vinylrecycling.com, Umincorp—all Dutch firms—all declared bankruptcy, adding to the tally of seven Netherlands plant closures in 2024.
-
Nov 2024 -- Suez, Loop Industries and SK Geo Centric were forced to abandon a large scale PET chemical recycling project in Saint-Avold, France, that was announced in February 2023.
-
Nov 2024 -- Viridor announced mechanical recycling plant closures both at Avonmouth and Rochester (total capacity 155,000 tonnes, £317 million invested).
-
Oct 2024 -- Ioniqa filed for bankruptcy protection as production costs overwhelmed revenues. The company had developed an ionic liquid–catalyzed PET glycolysis process (10,000 tonnes demo plant capacity). The company announced a restart in December 2024 after shedding half of its employees, closing the Geleen facility and focusing solely on selling licenses.
-
Oct 2024 -- PVC Recycling Lelystad (processing capacity of 20,000 to 30,000 tonnes of PVC waste) and others have ceased operations, with auctions of machinery showing a sector in distress.
-
Mar 2024 -- Borealis announced to put on hold the Stenungsung pyrolysis project (50,000 tonnes of pyrolysis oil), backed by a grant from the Swedish Energy Agency (SEA) and that was expected to begin operations in 2024.
-
Jan 2024 -- Umincorp Polymers BV, a Dutch recycling company, was declared insolvent. The company had previously declared that its recycled materials produced at the Rotterdam facility (36,000 tonnes of PET bottles recycling capacity) were no longer competitive - in terms of price - with the virgin materials on the market.
-
Dec 2023 -- Veolia shut down its PET recycling operations in Rostock (32,000 tonnes of food-grade recycled PET) at the end of 2023 after more than 20 years of operation owing to economic pressures.
-
Sep 2022 -- Recycling Technologies, former partner of Plastics Europe for plastics pyrolysis, entered administration following an unsuccessful process to seek additional investment after receiving £2 million from Zero Waste Scotland, strucking deals worth
£65 million for the forward sale of py-oil and the backing by Swindon borough council with upwards of £10 million in grants and investment rounds.
-
Feb 2022 -- The Advanced Plastic Purification International (Appi) will not build a chemical recycling plant in the port of Ostende, Belgium. The project, which was planned to process 500,000 tonnes of plastic waste annually on a 15-hectare site in the "Plassendale" area of the port, has been abandoned.
This wave isn’t isolated. EUWID Recycling reports dozens of closures and receiverships across Germany, the Netherlands, France, and the UK—signals of a deep-rooted crisis.
The Scope: Billions Invested—Hundreds of Thousands of Tonnes Gone
Industry analysis suggests at least 600,000 tonnes/year of recycling capacity have vanished since 2023—a figure likely understated, considering bankrupt auctions, idle plants, and stillborn projects not itemized in public records.
Why the Recycling Renaissance Failed
Why did all this money, all these policies, and such grand ambition crash so dramatically? The answer is found in the economics of plastics, energy, and global markets.
Virgin Plastic: The Irresistible Competitor
From 2023 onward, virgin plastic prices plummeted as mega-plants in China, the Middle East, and the US began pumping out vast quantities. Europe’s recycled plastics faced a relentless flood of cheap, imported virgin material. By February 2025, recycled PET averaged $750-800 per tonne more than virgin PET, shutting recycled product out of mass markets.
Imports Add Insult to Injury
Europe, meant to be the greenest market, found itself increasingly buying cheap, sometimes dubiously labeled “recycled” plastics from abroad—often without effective verification. Domestic recyclers couldn’t compete with imports made under looser standards, lower labor costs, and less expensive energy.
The Energy Crunch
Recycling, especially chemical, is energy-intensive. Europe’s natural gas price surge post-2022 made recycling electricity 3–4x costlier than in the US. Energy went from 15% to over 50% of operating costs; some German operators report 70% of costs are now electricity. Italy and Germany both saw recyclers shut simply because the utility bill made month-to-month survival impossible.
Subsidies and Taxes: Not Enough, Sometimes Hurting More
Public subsidies temporarily shielded recyclers from stark costs but couldn’t build businesses that last. The UK Packaging Tax, the Spanish tax on virgin plastics, the EU’s plastic tax (€0.80/kg on non-recycled waste) and other national fees on packaging raised costs for converters, reducing volumes. Grants like Re-Match’s in the Netherlands kept operations afloat for a season before insolvency struck.
The EU’s Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR), which imposes new targets and strict reporting, arrived just as the industrial base capable of meeting those targets collapsed. Uncertainty around regulation, rapidly shifting standards, and policy delays chilled new investment.
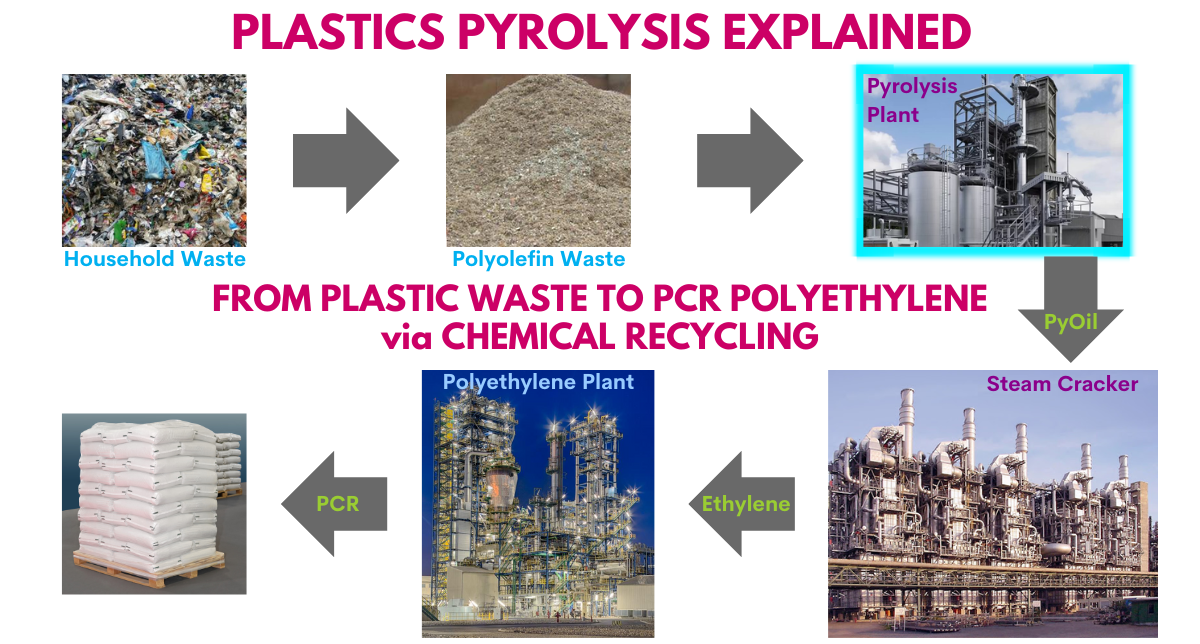
Chemical Recycling: Too Early for Profits
Once marketed as a technological fix for “unrecyclable” plastics, chemical recycling remains dogged by technical obstacles and astronomical costs. Reports show most commercial chemical recycling plants have failed to break even (Ioniqa, Blue Cycle, Fuenix Ecogy, Mura, Suez-Saint Avold, Neste/Ravago—all shuttered or cancelled).
A Downward Spiral: When Virgin Closes, Recycling Follows
Economics don’t favor recycling when even virgin resin production itself is being curtailed. Dow, Sabic, LyondellBasell, and others are closing or mothballing crackers and polymer lines in the EU as profits evaporate. For recyclers, those same factors—depressed demand, high costs—make new investment suicidal.
The Human & Environmental Cost
These closures mean lost jobs—sometimes entire regions losing “green economy” hopes as plants shutter mere months after opening. In the UK, each Viridor and Biffa closure meant over 100 direct jobs lost, plus suppliers and logistics implications. Across Germany, the Dutch industrial belt, and France, engineers and operators have been left stranded by the implosion.
Environmentally, it means less plastic recycled, more waste exported, and slower progress toward circular economy goals. In 2024, EU plastic waste exports rose 36% versus 2022; the continent was forced to send its problem abroad as recycling plants went idle.
How Did It Go So Wrong?
Ambitious European leaders thought that regulation, taxes, and subsidy would create an industry. Instead, they created a sector unable to survive outside artificial support, all while failing to acknowledge the fundamental economic disadvantage. The “subsidy trap” encouraged over-investment, triggering catastrophic losses for both private and public actors once market discipline returned.
Will Recovery Come?
Without radical changes in energy pricing, global competition rules, and technology, it’s hard to see a path back. Domestic demand is weak, policies are too volatile, and Europe’s cost base is increasingly uncompetitive.
A handful of survivors may limp on, but the dream of a self-sustaining, export-driven European recycling industry is dead for now. The future may bring new technology, smarter deposit schemes, and regulatory clarity, but that requires confronting the hard lessons of this exodus: only market-viable solutions will last.
And for now, the so-called circular economy remains just out of reach, as shuttered plants and bankruptcy filings mark the end of an era built on wishes, not on economic reality.
This report was compiled from dozens of recent sources, including C&EN, ChemAnalyst, EUWID Recycling, Troostwijk Auctions, Argus Media, ICIS, Sustainable Plastics, Zero Waste Europe, Resource Recycling, Chemical Recycling Europe, LinkedIn industry posts, as well as European Commission and regulator reports, in addition to build on ppPLUS own market intelligence.
#plasticwaste #plasticrecycling #chemicalrecycling #molecularrecycling #pyrolysis #depolymerization #pyoil #plastictax #ppwr






















































































































































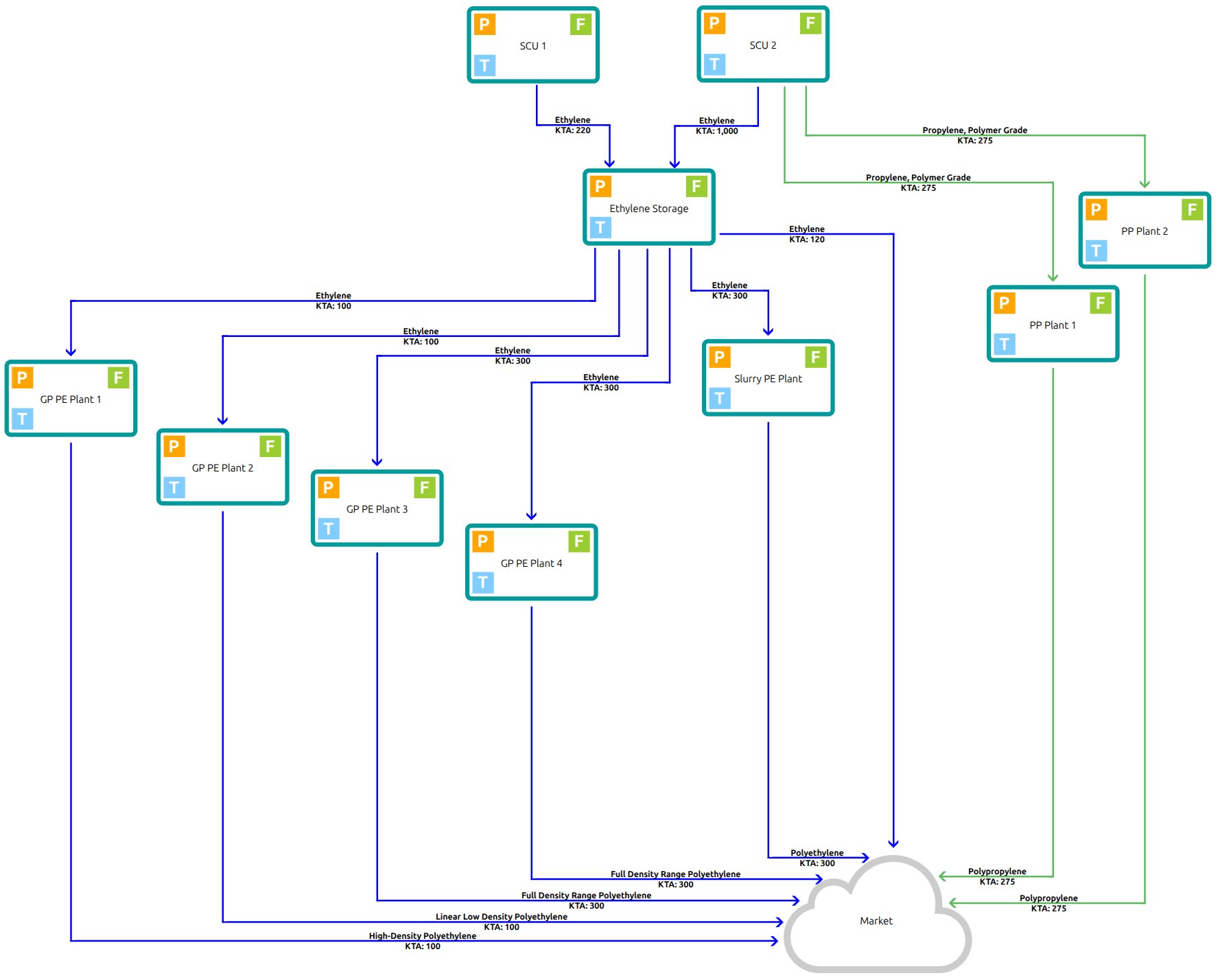




.png)



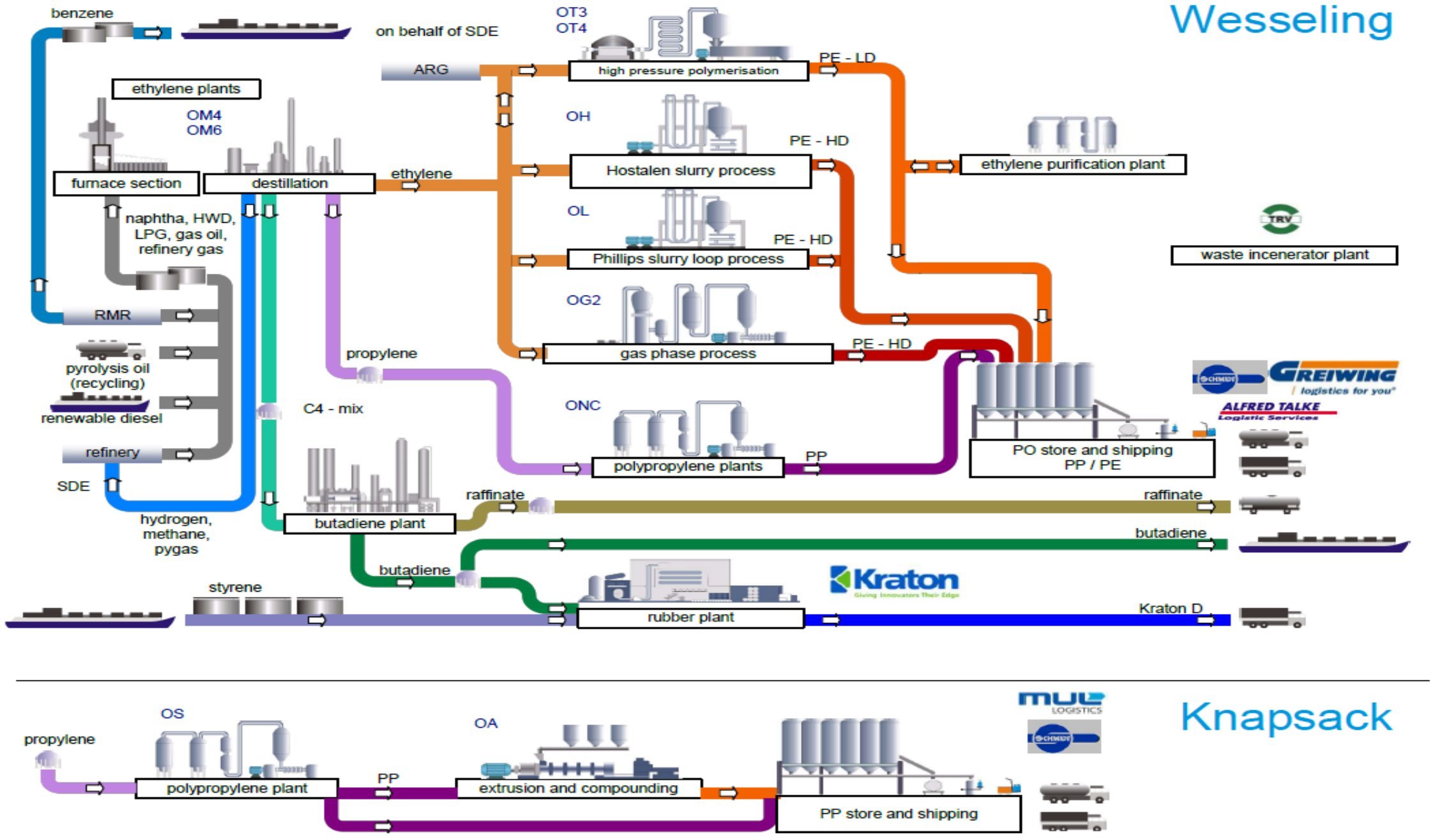
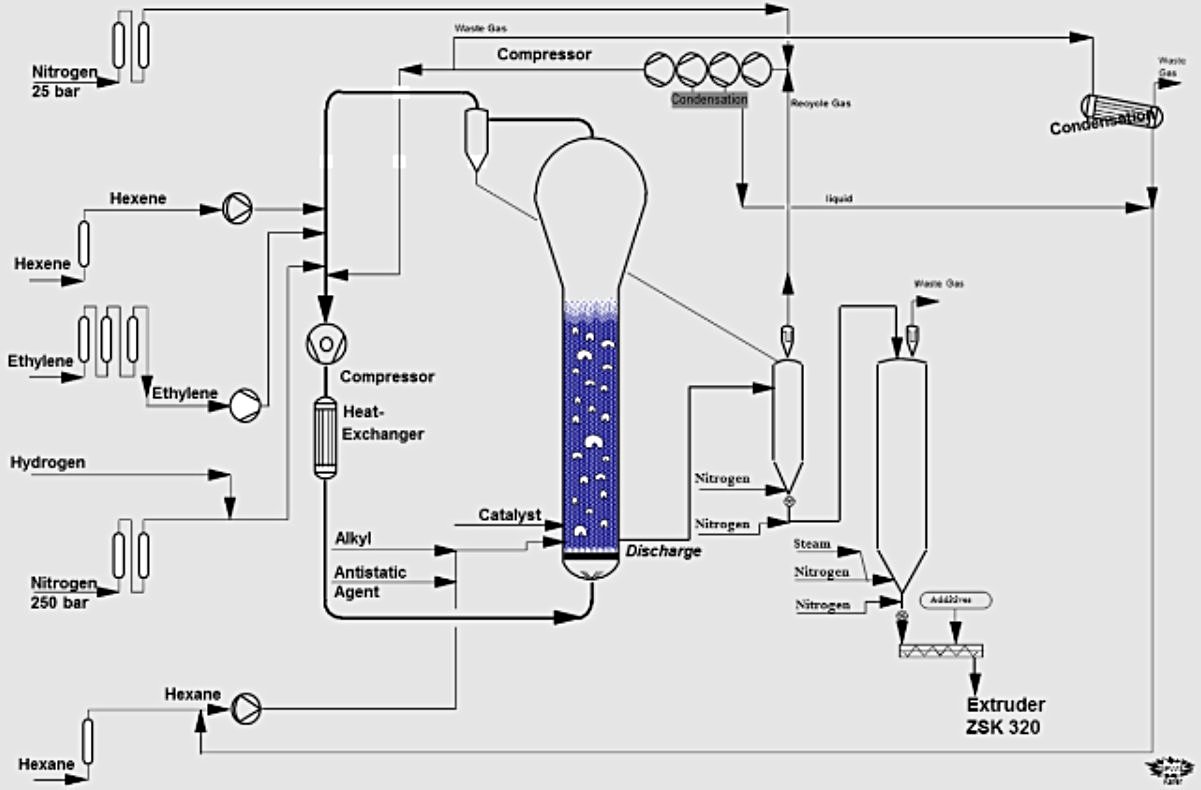





























































































































































































.jpeg)