Technology Type
- Type
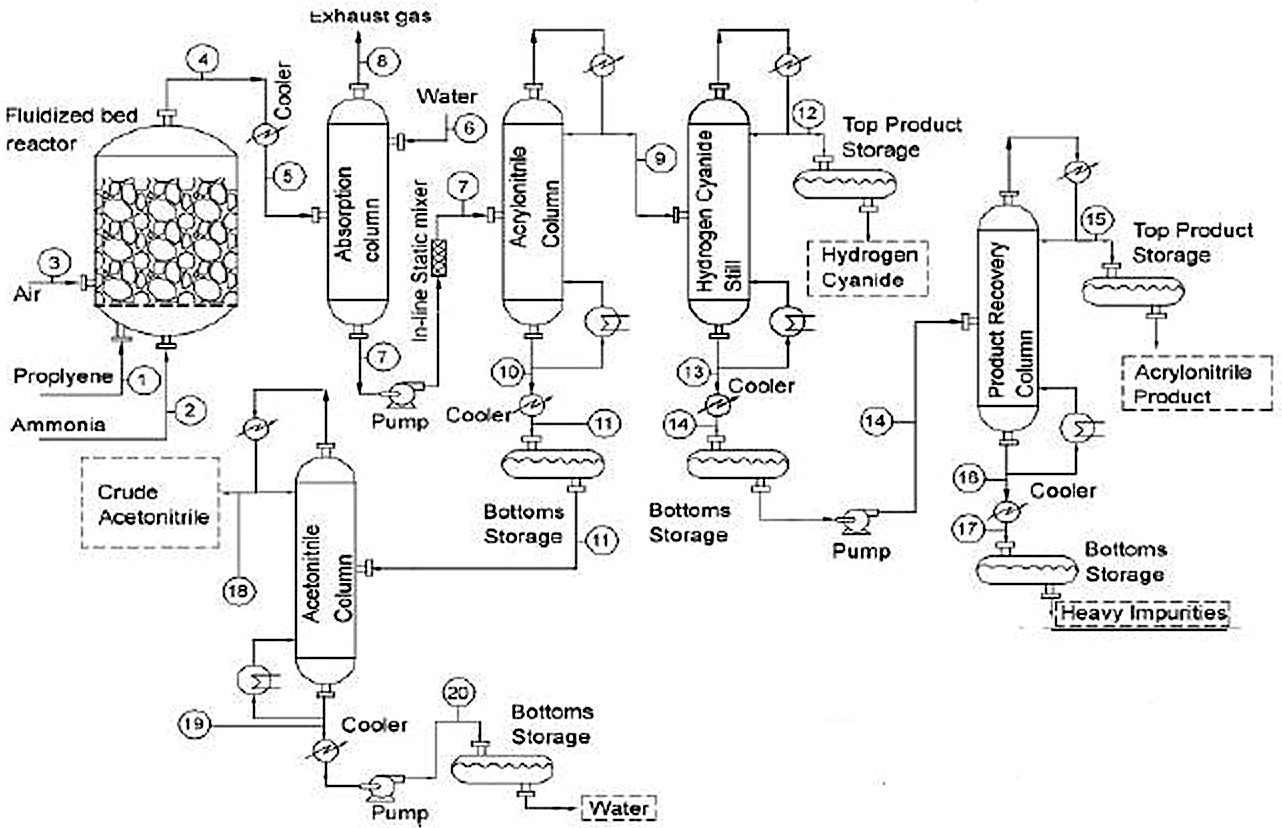
- Ammoxidation of Propylene into Acrylonitrile (SOHIO Process)
- Process
- Ammoxidation Reactions
- Abbreviation
- SOHIO
-

- #TT143
Description
Your insights will be shown here
Image
| Technology | Owner | Entity |
|---|---|---|

|
Ineos Techn Holdings |
Content provided by
| Transaction | Name | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Modified by |
|
3/21/2025 6:38 PM |
| Added | 3/21/2025 2:31 PM |