Overview
Badger ethylbenzene technology is used to produce ethylbenzene from benzene and either polymer-grade ethylene or an ethylene/ethane feedstock using the EBMax℠ process and proprietary alkylation and transalkylation catalysts available through ExxonMobil. The technology can be applied in the design of grass roots units, the revamp of existing vapor phase technology plants, or the conversion of aluminum chloride units.
Catalysts
The ExxonMobil zeolite catalysts are non-corrosive, environmentally inert, and regenerable. They are free-flowing before and after use and require no special packaging or handling. Offsite regeneration is largely the preferred method due to the long cycle length. These catalysts enable the plant to be constructed of carbon steel. The catalysts do not produce byproduct oligomers and can operate at extremely low benzene to ethylene ratios.
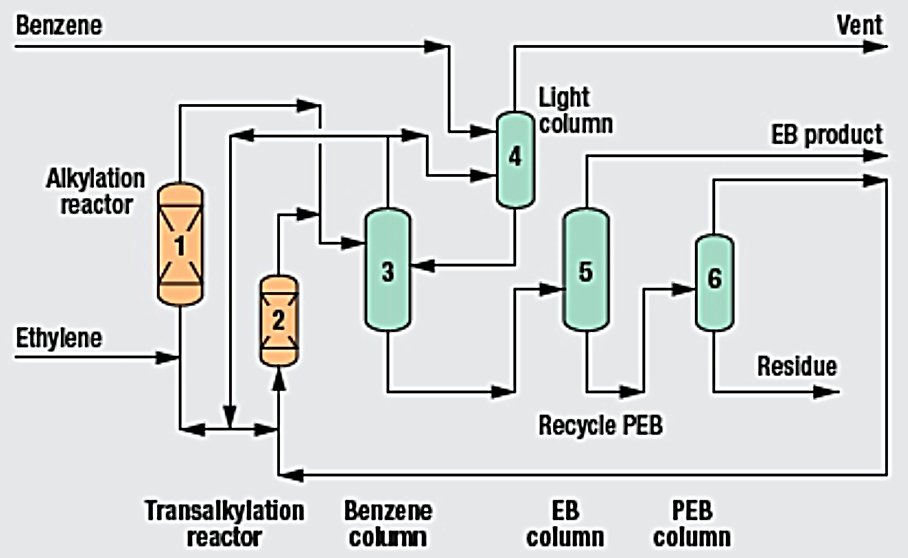
Process Flow Sheet (illustration)
Alkylation
Ethylene reacts with benzene in either a totally liquid-filled or mixed-phase alkylation reactor (1) containing multiple fixed-beds of ExxonMobil’s proprietary catalyst, forming EB and very small quantities of polyethylbenzenes.
Transalkylation
In the transalkylation reactor (2), the small amounts of polyethylbenzenes (PEB) formed in the alkylation reactor are converted to additional EB by reaction with benzene in the liquid phase over ExxonMobil’s transalkylation catalyst.
Purification
Effluents from the alkylation and transalkylation reactors are fed to the benzene column (3), where unreacted benzene is recovered from crude EB. The fresh benzene feedstock and a small vent stream from the benzene column are fed to the lights column (4) to reject light impurities. The lights column bottoms is returned to the benzene column. The bottoms from the benzene column is fed to the EB column (5) to recover EB product. The bottoms from the EB column is fed to the PEB column (6) where polyethylbenzenes are recovered as a distillate and recycled for conversion into EB in the transalkylation reactor, and heavy compounds are rejected in a bottoms stream that can be used as fuel.
Process Efficiency and Yields
- Guard bed catalyst removes traces of nitrogen-containing compounds which would otherwise poison the process catalysts, minimizing the frequency of catalyst regeneration.
- Zeolite alkylation catalyst does not age due to coking caused by ethylene oligomerization, resulting in long, uninterrupted EBMax unit operation.
- The alkylation catalyst is highly selective to monoalkylation, which has allowed operation at design benzene-to-ethylene molar feed ratios as low as 1.6-to-1 for plant expansion projects.
- The reaction system produces extremely low levels of impurities boiling in the range of EB, resulting in EB product purities in excess of 99.97 wt%.
- Ultra-high (nearly stoichiometric) yields minimize raw material consumptions.
Commercial Experience
- As of early 2024, plants using Badger Ethylbenzene technologies produce over half of the world's ethylbenzene capacity having a total installed capacity of more than 26 million metric tonnes per year.
- Single trains as large as 1.4 million MTA have been demonstrated.
- Badger and ExxonMobil assist producers with troubleshooting, plant monitoring, and potential plant expansions.
References
- Jack, 5th June 2018, Ethylbenzene Process by Badger Licensing LLC, Oil & Gas Process Engineering.
- Badger Licensing > Technologies > Technoloogies Licensing > Ethylbenzene. (accessed 20 Apr 2025)