Product
- Product
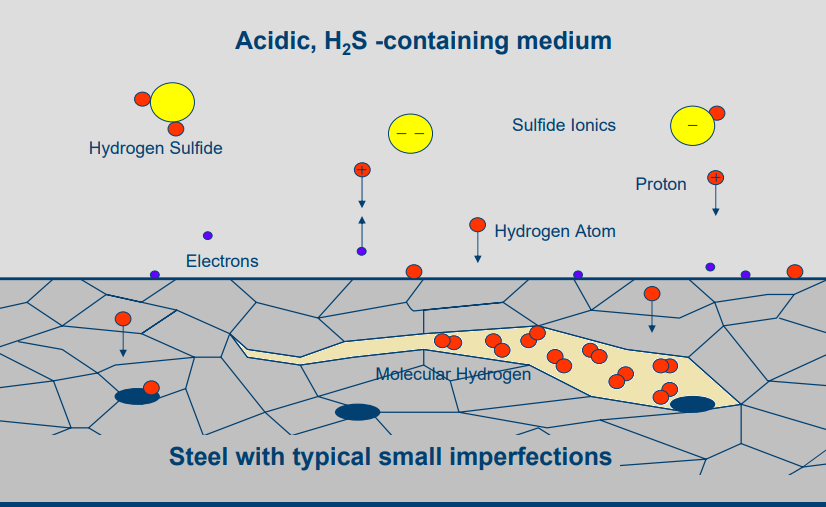
- Sour Gas
-

- #PS170
- Main Product
- Natural Gas
- Segment
- Extractive Industry Products
- Main-Family
- Fossil Hydrocarbons
- Sub-Family
- Gaseous Feedstock
- Physical State
-
Gas
Description
Your insights will be shown here
Product Communicator
| Title | Date | |
|---|---|---|

|
8/8/2025 |
Identifiers
No Identifiers defined
Chemical Data
- Molecular Weight (g/mol)
- 20
- Sulfur Content (wt%)
- 3
- Specific Gravity
- 0.65
Crude Data
- API Gravity
- 86.19230769230768
- Country
Product Settings
- Default
- Status
- A
Content provided by
| Transaction | Name | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Modified by |
|
8/8/2025 2:38 PM |
| Added by |
|
10/8/2021 6:43 AM |