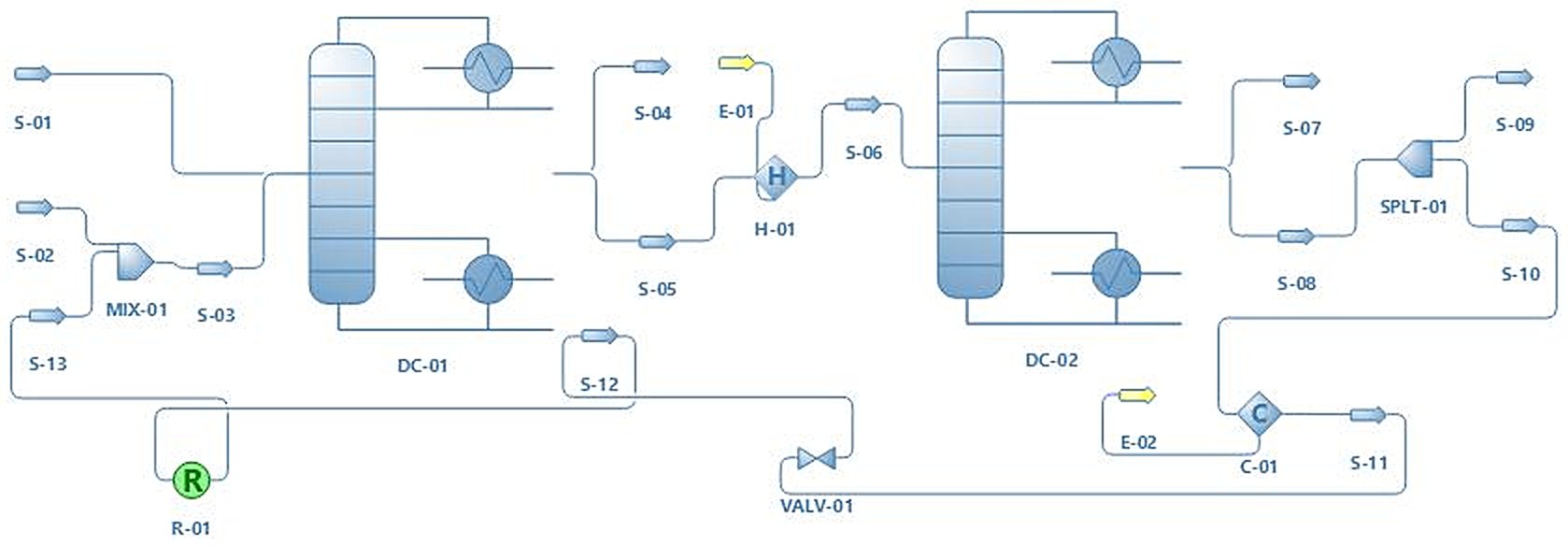
Technology

- Name
- Axens Butene-1 Superfractionation
- Owner
-
/ Axens SA - Brand
- Process
- Separation Processes
- Type
- Butane and Butenes Separation from C4 Raffinate Streams
- Available
-

- #TE351
Description
Your insights will be shown here
| Technology Unit |
|---|
| Distillation Column |
| Heat Exchanger |
| Mixer |
| Reboiler |
| Splitter |
| Stripping Column |
| Entity | Site (Country) | Asset (Plant) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|
|
1-Butene Plant | ||

|

|
|
Butene-1 Unit |
Content provided by
| Transaction | Name | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Modified by |
|
8/2/2025 7:35 AM |
| Added by |
|
8/1/2025 4:39 PM |