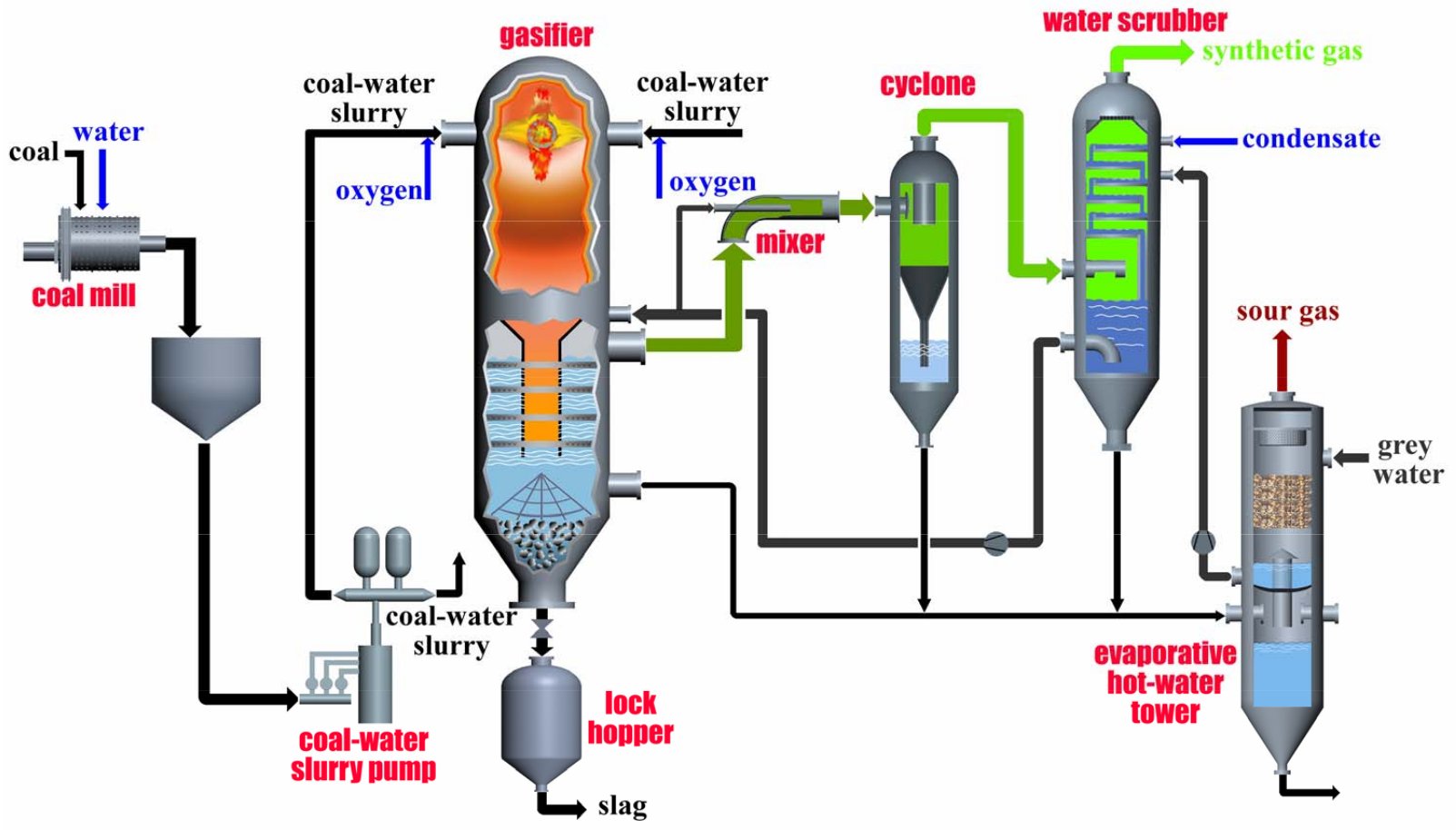
The Opposed Multi-Burner (OMB) Coal-Water Slurry (CWS) Gasification technology, developed by the East China University of Science and Technology (ECUST), represents a leading entrained-flow gasification process optimized for efficiency and scalability.
Process History
- Development: Initiated in the early 1990s by ECUST's Institute of Clean Coal Technology (ICCT) in collaboration with Yankuang Group.
- Milestones:
- 2000: Successful pilot operation (22 t/d capacity) at Lunan Chemical Fertilizer Plant.
- 2004: First commercial deployment (750 t/d) at Hualu Hengsheng Chemical Co., Dezhou.
- 2005: Second commercial unit (1,150 t/d) operational at Guotai Company of Yankuang Group.
- 2006–2010: Technology scaled up 2,000 t/d and implemented in multiple plants.
- 2011–2015: Further scale-up to 3,000 t/d, with several plants commissioned at this capacity.
- 2013: Officially designated a "world-class technology" by China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Association.
- 2019: World's largest single OMB gasifier (4,000 t/d) put into operation at Rongxin Co., Ltd, Inner Mongolia.
- Dec 2020: China's first radiant syngas cooler (RSC) combined with quenching chamber OMB gasifier (2,000 t/d) started up in Yulin, Yankuang Co., Ltd.
- End of 2020: OMB technology applied in 63 enterprises, 187 gasifiers under construction or operation worldwide.
Figure 1 - Milestones of OBM CWS Gasification Technology Development

Process Summary
The technology involves processing syngas from raw materials such as pure oxygen and coal-water slurry. The technical characteristics of the technology include:
- OMB coal-water slurry entrained-flow gasifier and compound-bed gas washing and quenching equipment.
- Three-unit combination comprising the mixer, cyclone, separator, and water scrubber of the preliminary purification process for syngas.
- Direct heat exchange-type wastewater treatment and heat recovery technology for evaporative separation.
Process design and characteristics:
- Core Design: Entrained-flow gasifier with symmetrically opposed burners (typically 4), enabling turbulent mixing and high reaction efficiency.
- Feedstock: Coal-water slurry (60–65% coal) and oxygen.
- Operating Conditions:
- Temperature: 1,300–1,400°C.
- Pressure: up to 6.5 MPa.
- Output: Syngas (CO + H₂) for chemicals, fuels, or power generation.
- Key Innovations:
- Water-quench cooling for slag handling.
- Refractory-lined reactor for thermal stability.
The OMB coal-water slurry gasifier (Fig. 2) has four symmetrical burners, located at the upper part of the gasifier chamber. This type of opposed impact gasifier overcomes the flaw of irrational residence time distribution in the single-burner coal-water slurry gasifier, as well as short residence time of partial reaction materials in the gasifier. The result is an improvement in gasification efficiency.
Figure 2 - OBM coal-slurry water Gasifier
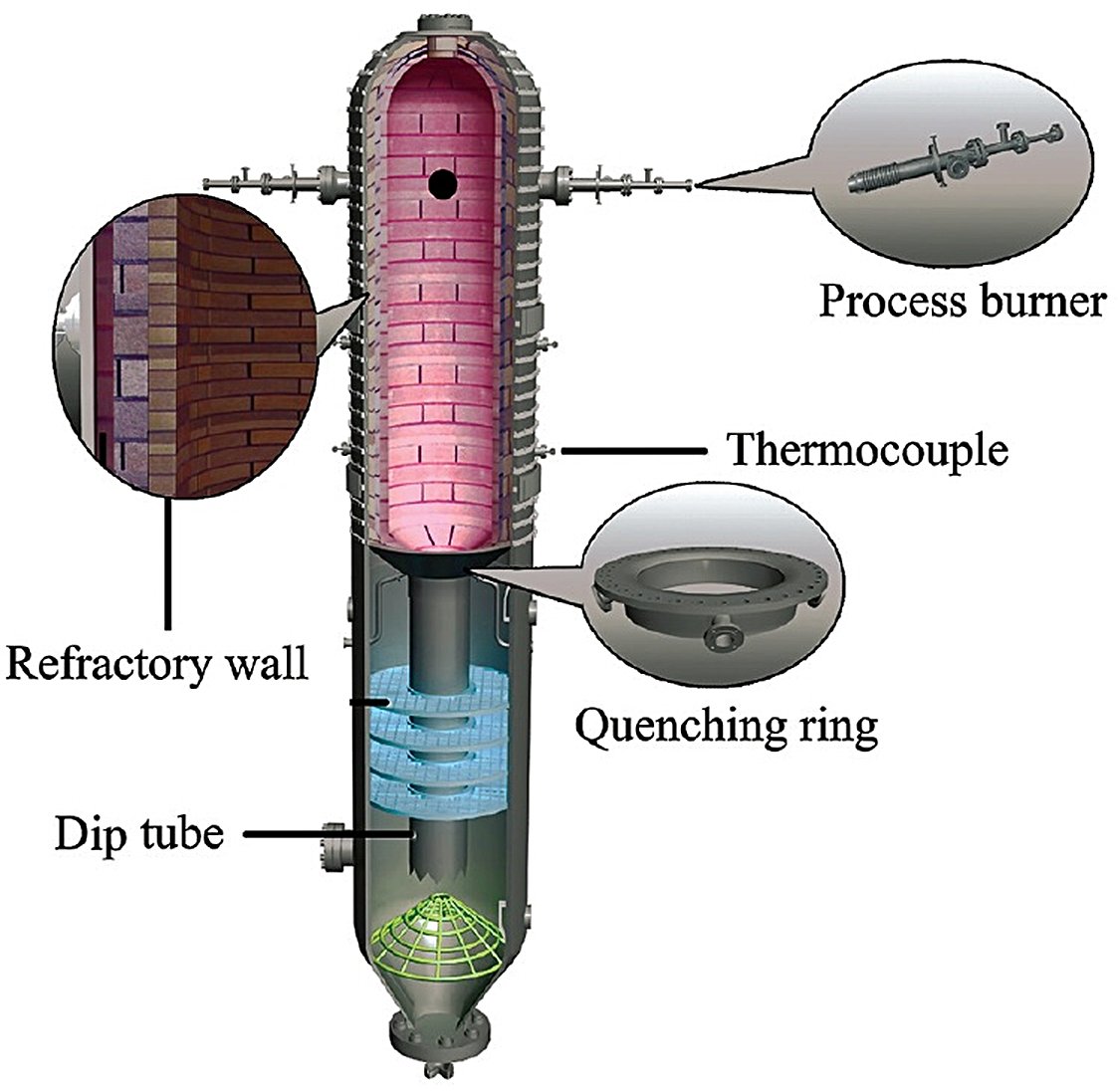
Detailed Process Flow
- Feed Injection:
CWS and oxygen injected via opposed burners into the gasification chamber.
- Reaction Zone:
Coal undergoes pyrolysis, combustion, and reduction at 1,300–1,400°C.
- Quenching:
Syngas cooled to ~190°C via water quench ring and submerged dip tube.
- Syngas Cleaning:
Cyclonic separation and water scrubbing remove particulates/tars.
- Slag Handling:
Molten slag solidifies in quench bath; removed via lock hopper.
Key Parameters:
| Parameter |
Value |
| Coal Feed Rate |
750–4,000 t/d |
| Oxygen Consumption |
360–410 Nm³/1000 Nm³ (CO+H₂) |
| Coal Consumption |
520–640 kg/1000 Nm³ (CO+H₂) |
| Carbon Conversion |
>98.5% |
Process Efficiency and Yields
- Capacity Range: 750–4,000 t/d per gasifier.
- Syngas Composition: 80–83% (CO+H₂) for CWS feed; 90–95% for dry-feed variants.
- Cold Gas Efficiency: 70–80%.
- Mass/Energy Balance:
- High carbon conversion (>98.5%) minimizes coal waste.
- Quench system recovers heat for steam generation.
- Comparative Advantage: Claimed to provide 7–9% higher syngas yield than Air Products (GE/Texaco) gasifiers at similar oxygen consumption.
Process Economics
- Capital Costs:
- Operating Costs:
- Cost of Electricity (COE): $281/MWh (5 MWe scale); drops to $137/MWh at 25 MWe due to economies of scale.
- Economic Drivers:
- Lower oxygen consumption vs. competitors (e.g., Shell, Air Products).
- Scalability to 4,000 t/d reduces per-unit costs.
Commercial Experience and Deployments
As of 2020, 31 projects (85 gasifiers) were operational globally, with 68 more under construction in China, the US, and South Korea.
Major ECUST OMB CWS Gasifier Projects:
| Company/Project |
Nr. of Gasifiers
& Capacity |
Syngas Flow Rate |
Start-up Date / Status |
| Hengli Petrochemical (Dalian) Refinery |
5 + 1
× 3,000 t/d |
1,000,000 Nm³/h |
Feb 2019 / Operational |
| Zhejiang Petrochemical (Zhoushan) Phase I & II |
8 + 4
× 3,000 t/d |
1,400,000 Nm³/h |
Nov 2019 / Operational |
| Inner Mongolia Rongxin Chemical |
2 + 1
× 4,000 t/d |
420,000 Nm³/h |
Oct 2019 / Operational |
Key Applications
- Chemicals: Ammonia, methanol, olefins (e.g., Yankuang Group plants).
- Fuels: Coal-to-liquids (CTL), hydrogen production.
- Power: IGCC projects (e.g., Yantai 300MW plant).
References
- Yu Zunhong et al., Research Institute of Clean Coal Technology, East China University of Science and Technology, Jan 2005 Presentation, Shanghai, Coal Gasification Technology in China: Application and Development.
- East China University of Science and Technology (ECUST), 14th May 2013, ECUST Technology labeled as World-class.
- National Energy Technology Laboratory (NETL), ECUST Gasifier, and references comprised therein.
- Haifeng L, Gong X*, Guangsuo Y, Wang F, Haifeng L, Wang Y and Xueli Chen, Recent Technology Advancement of ECUST Gasification Process, Recent Advances in Petrochemical Science, Vol. 2 Issue Jun 2017. DOI: 10.19080/RAPSCI.2017.02.555584
- Wang Fuchen, Yu Guangsuo, Guo Qinghua, 12th Apr 2017, Development of Coal Gasification Technology in China, CoalZoom.com.
- Trimeric Corporation, Report DE-FE0031506 published on U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), Office of Scientific and Technical Information (OSTI), Preliminary Technoeconomic Analysis for Power Generation from Coal Water Slurry Using Modular Staged-OMB Gasifier, retrieved via the Web Archive. (Document date: 28th May 2021)
- Zhang S, Dai Z, Xu J, Liu H, Wang F. Sensitivity and safety boundary Analysis of Opposed Multi‐Burner Coal Water Slurry Gasification System. Int J Energy Res. 2020;44:2278–2288.
- Wang F, Yu G, Liu H, Li W, Guo Q, Xu J, Gong Y, Zhao H, Lu H, Shen Z. Opposed multi-burner gasification technology: Recent process of fundamental research and industrial application. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2021. .
- School of Resources and Environmental Engineering, 18th Nov 2020, New Achievements on Opposed Multi-Burner Coal Water Slurry Gasification Technology.
- Qinghua Guo, 24th Jun 2020, Eat China University of Science and Technology (ECUST), Presentation: OMB Coal-Water Slurry Gasification Technology and Its Applications.