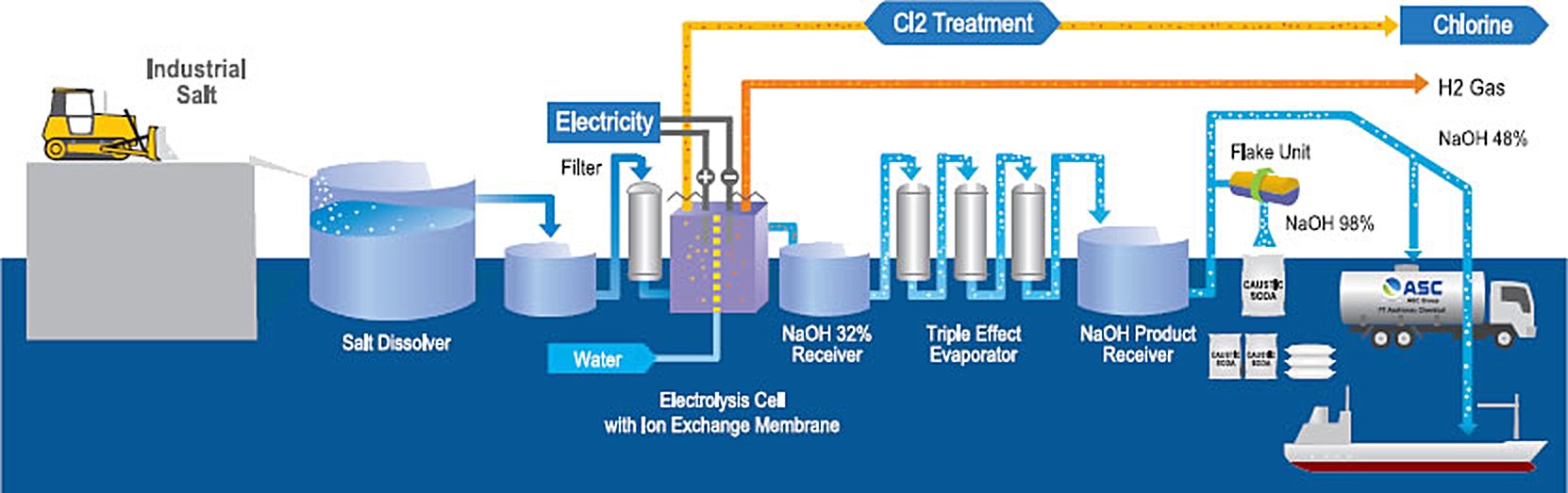
In the Chlor-Alkali Process, caustic soda is the main product along with chlorine gas, hydrogen gas and sodium hypochlorite solution as by-products.
In the Chlor-Alkali plant, common salt (sodium chloride, NaCl) is dissolved in water and purified. The purified concentrated salt solution is then electrolyzed utilizing the sophisticated cationic exchange membrane technology developed by AGC Inc. (Formerly Asahi Glass Company) to produce caustic soda, chlorine gas and hydrogen gas. Sodium hypochlorite is a derivative product obtained by reacting caustic soda and chlorine. ASC enjoys the benefit of the most environmentally friendly Chlor-Alkali technology consuming minimum energy, producing no pollution and delivering superior product quality.
Figure 1 - AGC Chlor-Alkali Process Block Flow Diagram[2]
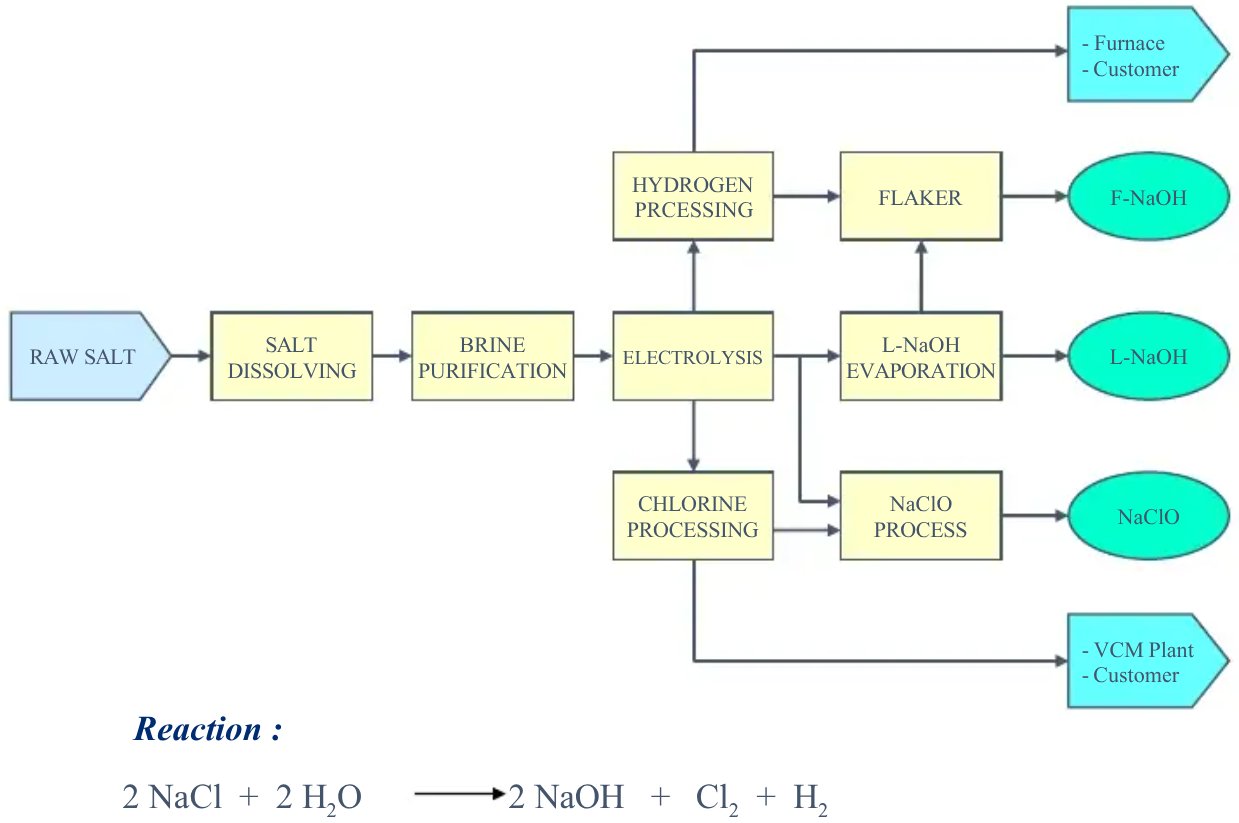
ASC Chlor-Alkali process makes use of cation exchange membrane technology, which is the most advanced, very efficient and the most environmentally friendly chlor alkali technology producing high quality products fulfilling a wide range of demanding applications. The chlor-alkali process involves the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride (NaCl solution or brine) in a membrane cell producing chlorine (Cl2) and its co-products caustic soda (sodium hydroxide, NaOH) and hydrogen gas (H2).
Figure 2 - Electrolysis system, using AGC’s ion-exchange membrane (Forblue™ Flemion™)[3]

In the membrane cell, the anode chamber and cathode chamber are separated by a cation-permeable membrane. Saturated brine (NaCl solution) which consists of Na+ and Cl– ions is fed to the anode chamber.
A DC current is passed through the cell.
At the anode, the chloride ions (Cl–) in brine solution (NaCl) are oxidized to chlorine (Cl2):
2 NaCl (aq) + 2 H2O (l) → 2 NaOH (aq) + Cl2 (g) + 2 H+ + 2 e–
And at the cathode, hydrogen ions (H+) in water is reduced to hydrogen gas (H2):
2 H+ + 2 e– → H2 (g)
The ion-permeable membrane at the center of the cell plays the important role of allowing the sodium ions (Na+) in the anode chamber to pass to the cathod chamber where they react with the hydroxide ions (OH–) to produce caustic soda (NaOH).
The overall reaction for the electrolysis of brine is thus:
2NaCl (aq) + 2H2O (l) → Cl2 (g) + H2 (g) + 2NaOH (aq)
In this process, when salt is electrolyzed, 0.9 tonnes of chlorine is produced from one ton of salt.
References
- ASC Co. India, Chlor-Alkali Process. (Captured 2nd Apr 2022)
- PT Asahimas Chemical, ASC Process Overview For Bidding Rev, SCRIBD. (Uploaded on May 13, 2024)
- AGC Inc., Feb 2025, AGC Data Book (Corporate and Product Information).
- AGC Inc., 16th Jun 2022, IR DAY 2022 <DAY 2> Chemicals.