Methylene Diphenyl Diisocyanate (MDI) is a reactive chemical intermediate with the molecular formula C₁₅H₁₀N₂O₂ and molecular weight of 250.25 g/mol. It serves as an essential building block in the production of polyurethanes, urethane-prepolymers, and polyisocyanurate polymers across diverse industries.
Chemical Structure and Isomers
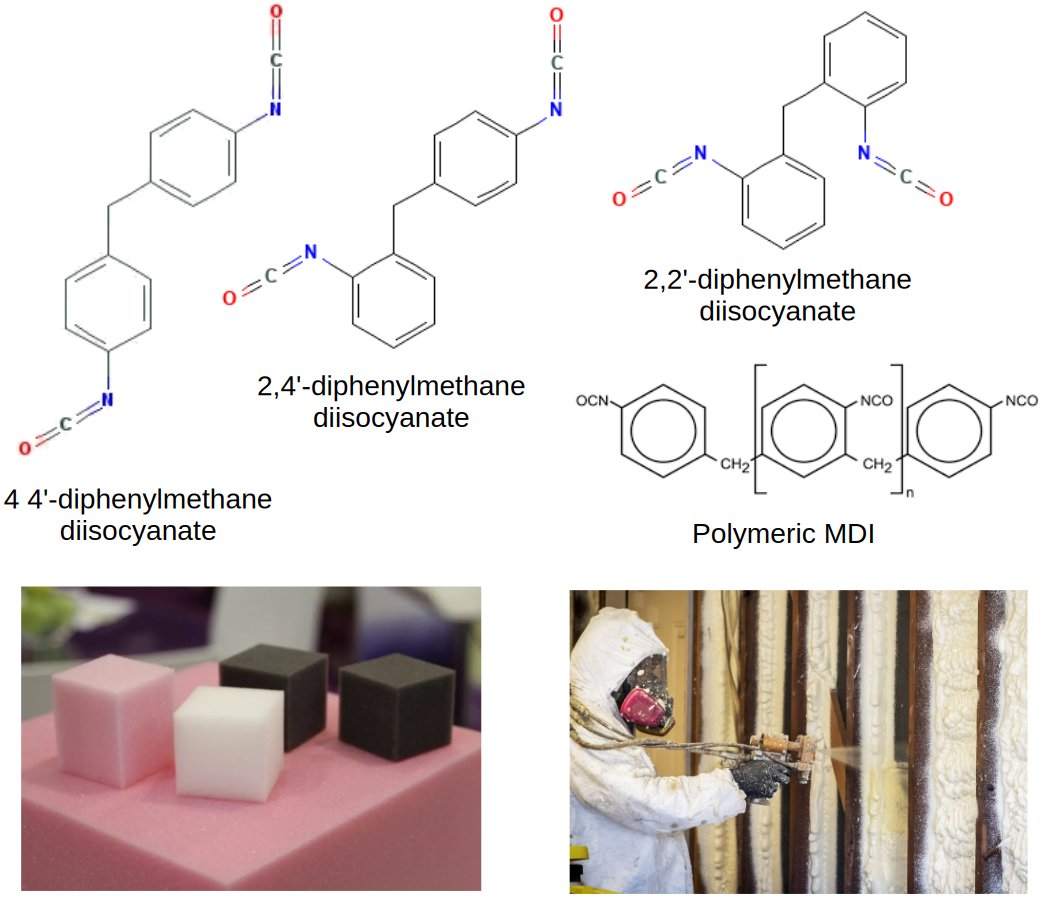
MDI exists in three main isomeric forms based on the positions of the isocyanate groups (-NCO) around the aromatic rings :
- 4,4'-MDI: The most commercially important isomer, also known as Pure MDI or Monomeric MDI (MMDI)
- 2,4'-MDI: Secondary isomer with differential reactivity
- 2,2'-MDI: Less common isomer
The 4,4'-MDI isomer appears as white to light-yellow, odorless flakes at room temperature with a melting point of 38-44°C. It becomes a clear, colorless to yellowish liquid when heated above 37°C.
Commercial Forms and Properties
Pure/Monomeric MDI (MMDI)
- White crystalline solid at room temperature containing >99.8% 4,4'-MDI
- NCO content of 33.6% with functionality of 2.0
- Exhibits high reactivity and linearity, making it ideal for spandex fibers, elastomers, and prepolymers
Polymeric MDI (PMDI)
- Dark brown to viscous liquid at room temperature
- Complex mixture containing 25-80% monomeric 4,4'-MDI plus oligomers with 3-6 aromatic rings
- NCO content of 30-32% with average functionality of 2.7 and viscosity of 150-250 mPa·s at 25°C
- Primary use in rigid and semi-rigid polyurethane foams for construction and insulation applications
Carbodiimide-Modified MDI
- Clear, light yellow liquid with functionality around 2.2 due to trifunctional uretonimine species formation
- Enhanced durability, hydrolysis resistance, and mechanical properties compared to standard MDI
- Used in automotive interior parts, steering wheels, and airbag covers
Production Process
MDI manufacture involves a two-step synthesis :
- Condensation Step: Aniline condenses with formaldehyde using hydrochloric acid as catalyst to produce methylenedianiline (MDA) and other diamine precursors
- Phosgenation Step: The diamines react with phosgene in a solvent to form raw MDI mixture, with solvent, excess phosgene, and hydrochloric acid by-products recovered and recycled
- Purification: Fractional distillation, crystallization, or sublimation separates polymeric MDI from pure MDI isomers
Key Physical Properties
| Property |
Value |
| Molecular Formula |
C₁₅H₁₀N₂O₂ |
| Molecular Weight |
250.25 g/mol |
| Melting Point |
38-44°C |
| Boiling Point |
392°C |
| Density |
1.19-1.23 g/cm³ |
| Vapor Pressure |
0.066 hPa at 20°C |
| Flash Point |
196°C |
| Water Solubility |
Insoluble; hydrolyzes in water |
Applications and Uses
MDI's versatility enables numerous polyurethane applications:
Foam Applications
- Rigid polyurethane foams for building insulation, appliance insulation, and construction panels
- Flexible foams for automotive seating, furniture cushioning, and mattresses
- Semi-rigid foams for automotive interior panels
Non-Foam Applications
- Coatings, Adhesives, Sealants, and Elastomers (CASE) products
- Thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPU) for automotive and industrial applications
- Spandex fibers and synthetic leather production
- Wood composite binders for particleboard and oriented strand board
Demand
MDI represents the most commercially important diisocyanate globally, with a demand exceeding 8.5 million tonnes annually as of 2024, a 6% increase from 2023, enabling the modern polyurethane industry's diverse applications.
References
- Methylene Diphenyl Diisocyanate (MDI) - Essential Building Blocks for Polyurethanes. Gantrade
- 4,4'-Diphenylmethane diisocyanate. ChemicalBook
- Jul 05, 2022.Polymeric MDI. Green View Technology and Development Co., Ltd.
- Polyurethane production in plastics & polymers production. KROHNE
- Jul 21, 2025. Methylene Diphenyl Diisocyanate (MDI) Market. Market Reports World.