Process Summary
Hydrodealkylation (HDA) is a chemical process that converts alkyl aromatic hydrocarbons to simpler aromatic compounds. One such reaction is the conversion of 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene to xylene. Toluene and xylenes can also be converted into additional benzene.This Chemical Process usually occurs at high temperature, at high pressure, or in the presence of a catalyst. These are predominantly Transition Metals, such as Chromium or Molybdenum[1].
Process Details
The aromatics recovered via the aromatics extraction process can be further processed through HDA if desired.
In case of toluene dealkylation into benzene, reactions taking place are depicted in Fig. 1. The primary reaction converts toluene to benzene and methane. A minor side reaction dimerizes benzene into diphenyl[2].
Figure 1 - Hydrodealkylation of Toluene into Benzene

In terms of technologies, two main approaches exist, thermal HDA and catalytic HDA.
1. Thermal HDA
The Thermal HDA process typically operates under these parameters:
- Temperature: 600-660°C[2]
- Pressure: 35-40 bar[2]
- Conversion: Typically 70%[2]
- Residence time: 1-10 seconds (to minimize by-products)[3]
- Hydrogen/hydrocarbon molar ratio: 0.5/1 to 10/1[4]
2. Catalytic HDA
Catalytic HDA process uses fixed bed or fluid bed catalysts such as alkali metals (10-30% by weight) or anhydrous supports (alumina, charcoal, magnesia)[4].
The Catalytic HDA process typically operates under the following parameters)[4]:
- Temperature: 600-1000°F (315-540°C)
- Pressure: 50-500 psig
- LHSV: 0.2-10
- Hydrogen/hydrocarbon ratio: 0.5:1 to
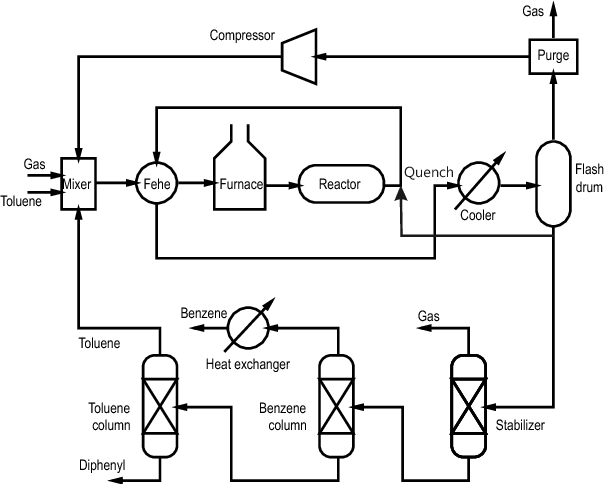
Process Configuration
The process typically includes)[2]:
- Feed mixing of toluene and hydrogen
- Preheating system
- Reactor section
- Heat recovery
- Product separation including:
- Flash separation
- Demethanizer
- Benzene recovery
- Biphenyl separation
References
- Wikipedia, Hydrodealkylation
- DWSIM, Sanagapalli Ventaka Karthik, 1st Jul 2018, Hydrodealkylation for Toluene, DWSIM
- Morgan C Sze, US3390200A, Priority Date: 24th Sep 1959, Production of aromatic hydrocarbons by hydrodealkyaltion and hydrogenolysis, Assigned to Lummus Technologies LLC, Status: Expired - Lifetime.
- A. Bergomi, US3751505A, Priority Date: 28th Mar 1972, Hydrodealkylation process, Assigned to: Goodyear Tire & Rubber Co., Status: Expired - Lifetime.