Product
- Product
- Light Aromatic Naphtha
- Abbreviation
- LAN
- Names
- Solvent naphtha (petroleum), light aromatic; Light aromatic solvent naphtha; C9-10 Aromatic hydrocarbons; C9 Aromatic naphtha
-

- #PS642
- Main Product
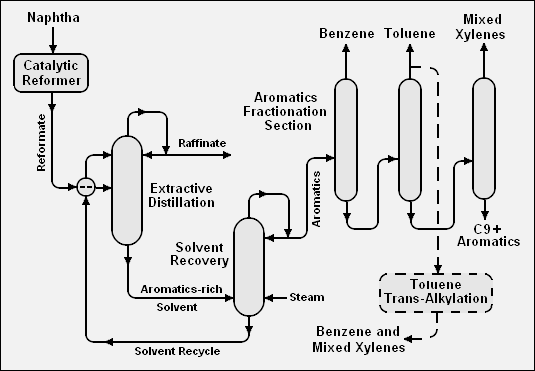
- Naphtha
- Segment
- Refined Products
- Main-Family
- Refinery Liquids
- Sub-Family
- Light Distll. & Proc. Hydroc.
- Physical State
-
Liquid
Description
Your insights will be shown here
Product Communicator
| Title | Date | |
|---|---|---|

|
1/3/2025 |
Identifiers
-
 CAS Number
CAS Number
- 64742-95-6
-
 EC Number
EC Number
- 265-199-0
-
 ECHA InfoCard
ECHA InfoCard
- 100.059.254
Chemical Data
- Chemical Formula
-
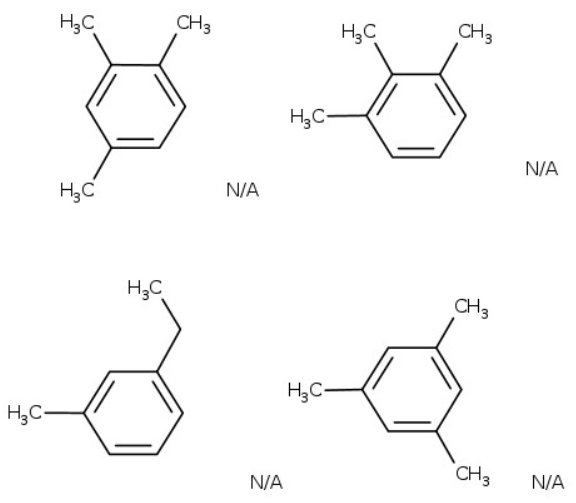
C9H12
- Molecular Weight (g/mol)
- 120.19
- Boiling Point (°C)
- 170
- Specific Gravity
- 0.87
Crude Data
- API Gravity
- 31.14
- Country
Product Settings
- Default
- Status
- A
Content provided by
| Transaction | Name | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Modified by |
|
1/4/2025 2:02 PM |
| Added by |
|
1/3/2025 8:45 PM |