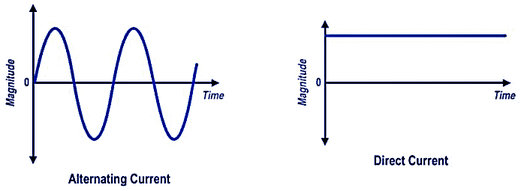
Electrical energy can be defined differently based on whether it involves AC or DC current:
Direct Current (DC) Electrical Energy
DC electrical energy is energy derived from the unidirectional flow of electric charge (electrons) through a conductor. Since DC maintains a constant direction and typically a steady voltage, the electrical energy in a DC system can be calculated using:
Energy = Power × Time
Where power (in watts) is calculated as P = IV (current × voltage). This formula applies to batteries, solar cells, and other DC power sources where electrons flow consistently from the negative to the positive terminal.
Alternating Current (AC) Electrical Energy
AC electrical energy comes from electric charge that periodically reverses direction and changes magnitude continuously with time. The energy in an AC system follows the same fundamental formula (Energy = Power × Time), but the calculation of power is more complex due to the sinusoidal nature of the current.
For AC, the effective power is calculated using RMS (root mean square) values:
Power = VRMS × IRMS
Where VRMS = Vpeak ÷ √2 for a sinusoidal waveform.
AC electrical energy is what's typically delivered to homes and businesses through power grids, while DC electrical energy is common in batteries, electronics, and some specialized applications like solar power systems.
The key distinction is that AC electrical energy involves oscillating power that averages over time, while DC electrical energy maintains a steady, unidirectional flow of power.