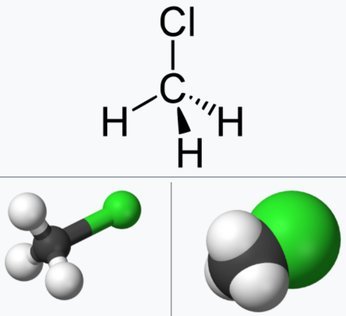
Chloromethane is a chemical compound of the group of organic compounds called haloalkanes. It is a colorless extremely flammable gas with a mildly sweet odor, which is, however, detected at possibly toxic levels. Due to concerns about its toxicity, it is no longer present in consumer products. It was once widely used as a refrigerant.
Most chloromethane is prepared by reacting methanol with hydrogen chloride, according to the chemical equation:
CH3OH + HCl → CH3Cl + H2O
This can be carried out either by bubbling hydrogen chloride gas through boiling methanol with or without a zinc chloride catalyst, or by passing combined methanol and hydrogen chloride vapors over an alumina catalyst at 350 °C (662 °F).
A smaller amount of chloromethane is produced by heating a mixture of methane and chlorine to over 400 °C (752 °F). However, this method also results in more highly chlorinated compounds such as methylene chloride and chloroform and is usually only used when these other products are also desired.
Further reaction of chloromethane with chlorine can produce dichloromethane, trichloromethane (known as chloroform) and tetrachloromethane (also known as carbon tetrachloride).
Source: Infogalactic, Chloromethane.