ROSE is a solvent deasphalting (SDA) process producing DAO and pitch from heavy feedstock streams
- Technology
- KBR ROSE
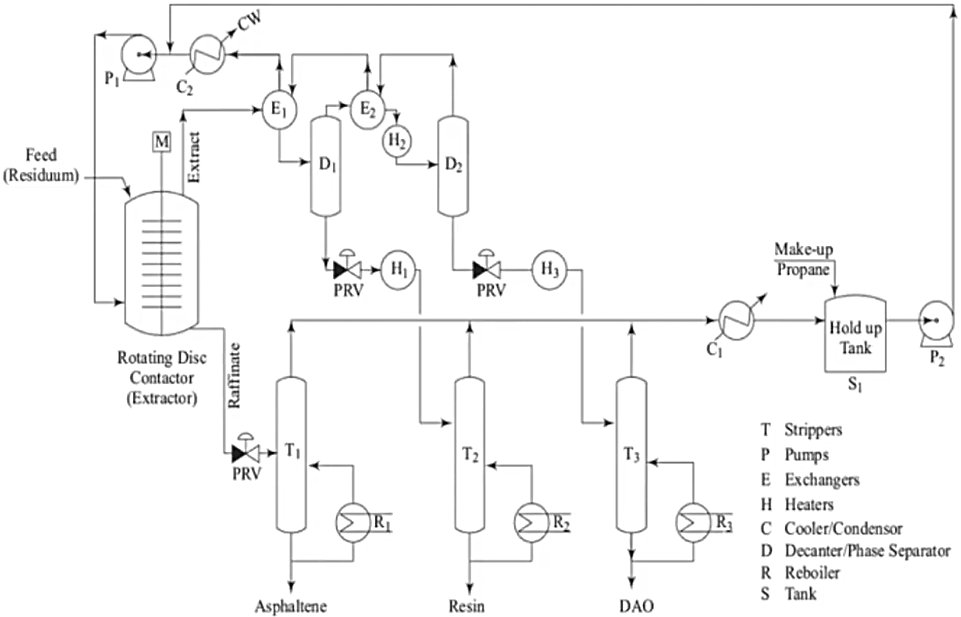
ROSE stands for Residuum Oil Supercritical Extraction. It is a solvent deasphalting (SDA) process developed and commercialized by Kerr-McGee Corporation, first licensed commercially in 1979, and acquired by KBR in 1995. The ROSE process uses a light paraffinic solvent under supercritical conditions to separate a heavy oil or residue feedstock — by molecular type rather than boiling point — into up to three product streams: Deasphalted Oil (DAO), Resins (in three-stage configurations), and Asphaltene Pitch.
Read the full ROSE technology profile here.
#rose #kbr #sda #solventdeasphalting #dao #deasphaltedoil #resin #pitch #bitumen #asphaltene






