Technology Type
- Type
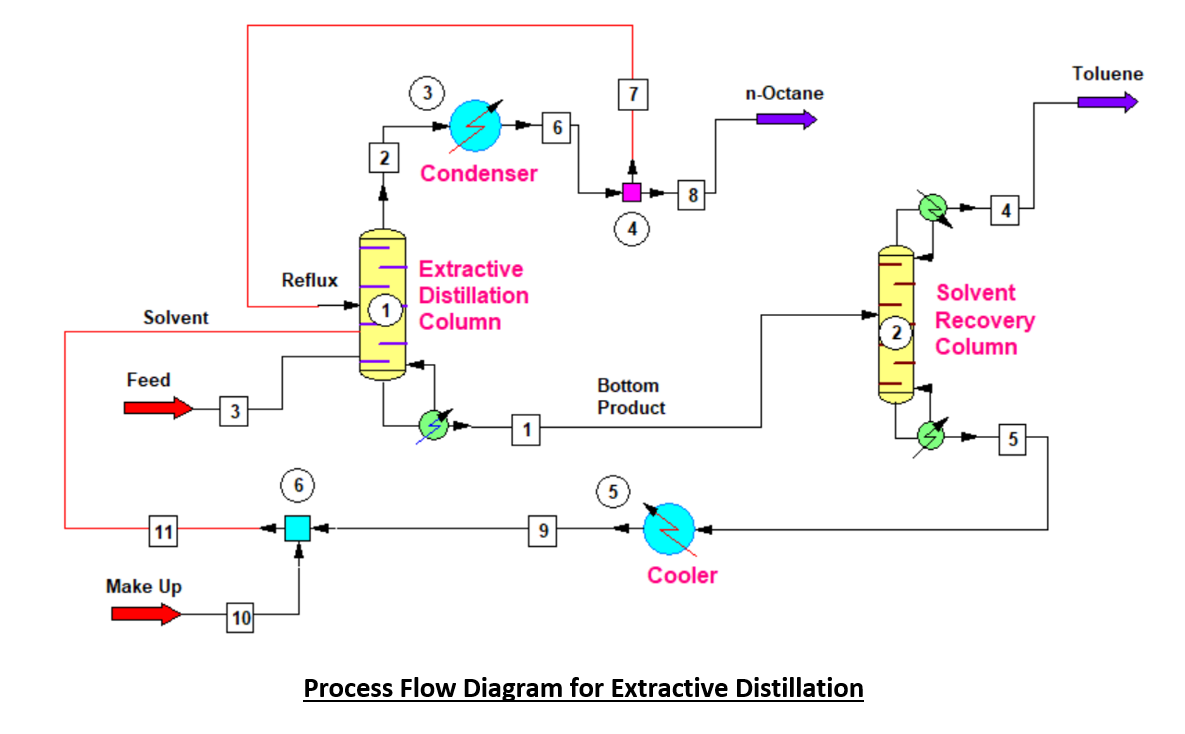
- BTX Separation via Extractive Distillation
- Process
- Separation Processes
-

- #TT49
Description
Your insights will be shown here
No entries
| Title | Date |
|---|
| Technology | Owner | Entity |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Air Liquide | |

|
SULZER | |

|
SULZER | |

|
Honeywell UOP | |

|
Honeywell UOP |
Content provided by
| Transaction | Name | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Modified by |
|
11/1/2025 9:12 AM |
| Added | 3/4/2022 5:32 PM |