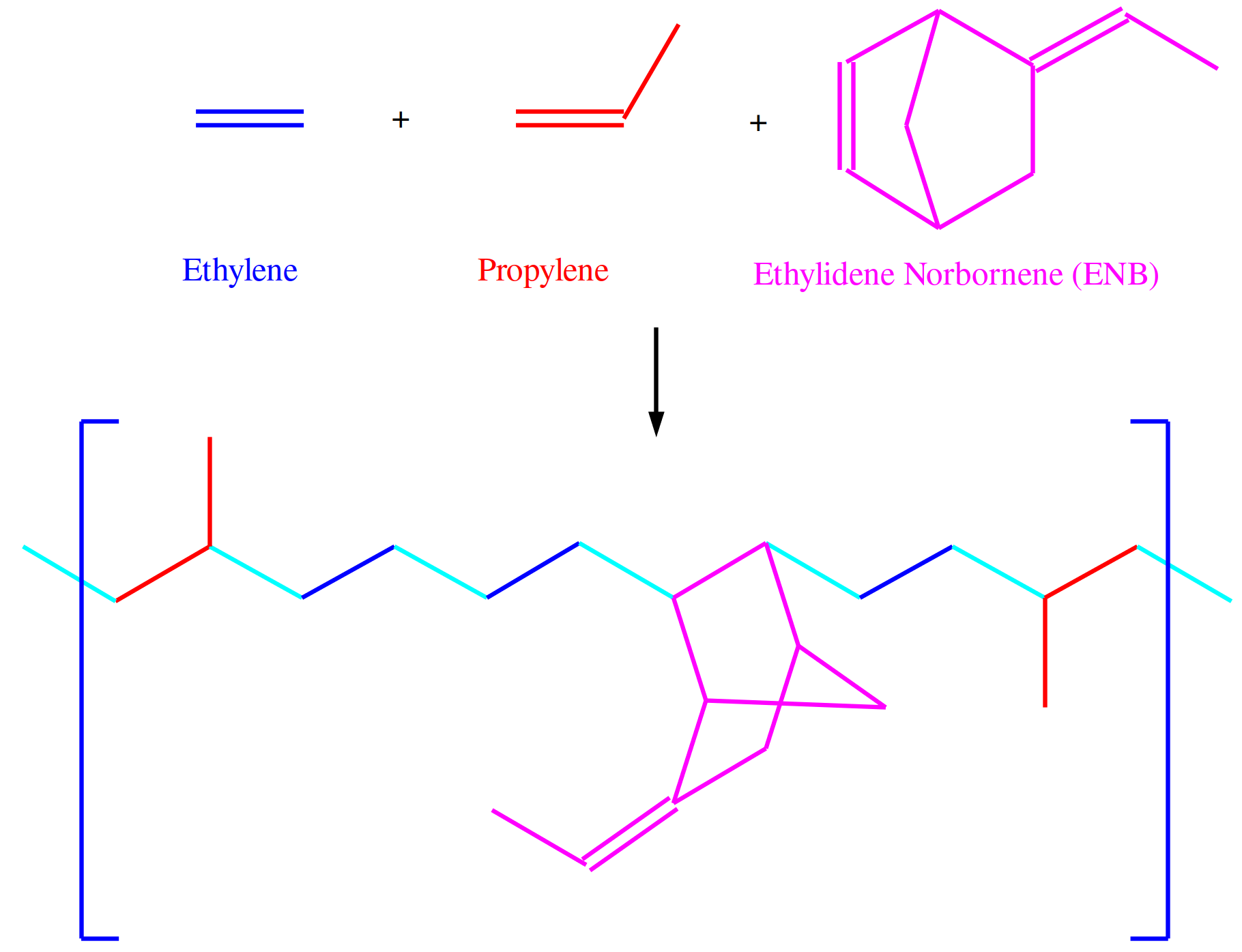
Technology Type
- Type
- EPR/EPDM Processes
- Process
- Synthetic Rubber Processes
- Link
-

- #TT28
Description
Your insights will be shown here
No entries
| Title | Date |
|---|
| Technology | Owner | Entity |
|---|---|---|

|
Sumitomo Chemical |
Content provided by
| Transaction | Name | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Modified by |
|
10/25/2022 2:10 PM |
| Added | 11/14/2021 6:46 PM |