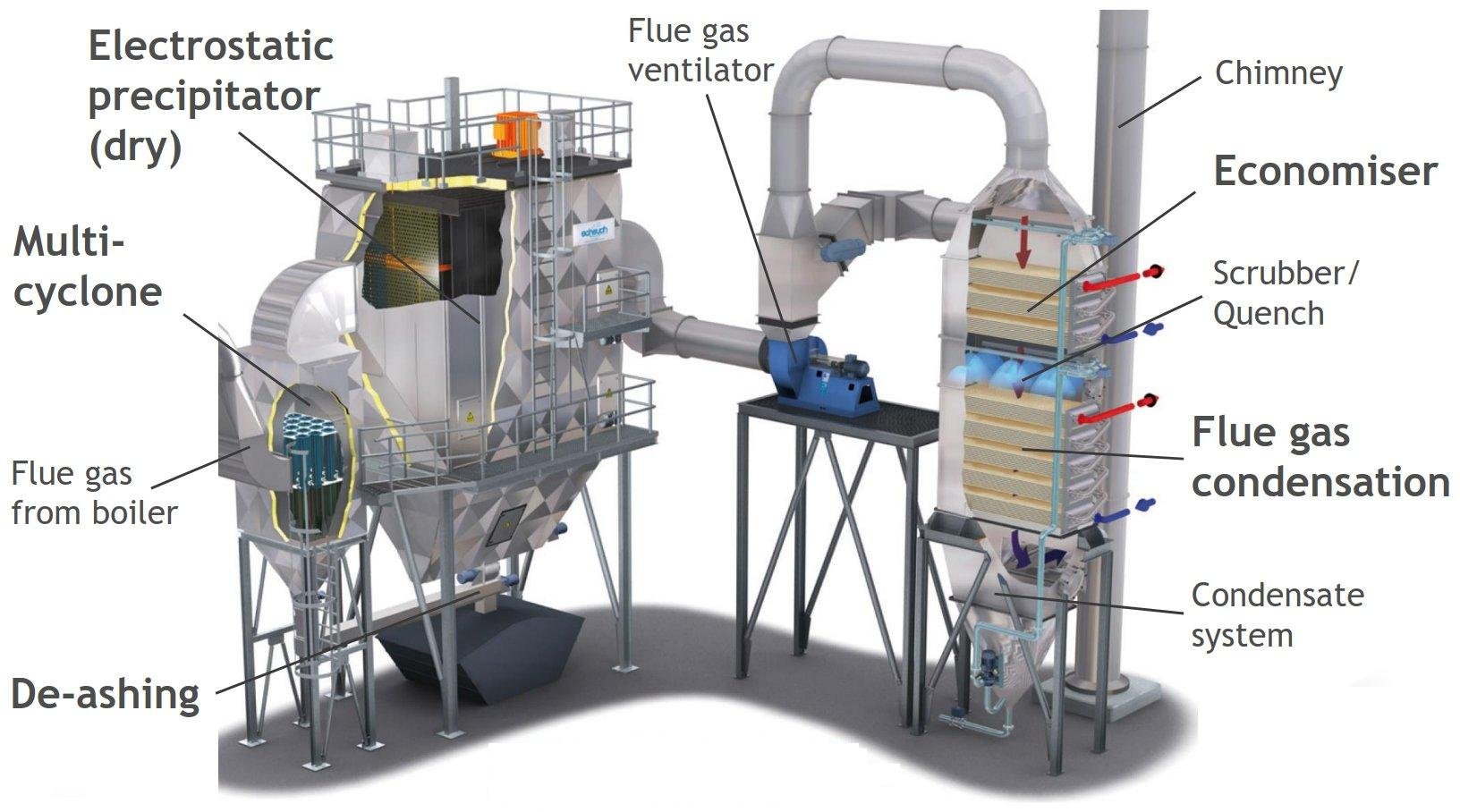
Flue gas cleaning is a comprehensive process designed to remove pollutants and hazardous substances from the exhaust gases produced by industrial combustion, such as those from power plants, waste incinerators, and biomass boilers. Its main goal is to ensure that emissions meet increasingly stringent environmental standards by targeting a wide range of contaminants, including particulates, acid gases (SOx, HCl, HF), nitrogen oxides (NOx), heavy metals, dioxins, furans, and sometimes mercury.
General Process Overview
1. Particulate Removal
- Initial cleaning typically involves devices such as cyclones, multi-cyclones, electrostatic precipitators (ESP), or baghouse filters to remove coarse and fine dust particles from the flue gas.
- Fabric filters (baghouses) can achieve dust separation efficiencies above 99.95%.
2. Acid Gas Neutralization
- Acidic components like SO2, HCl, and HF are neutralized using injected reagents such as sodium bicarbonate, hydrated lime, or limestone.
- This can be done via dry, semi-dry, or wet methods:
- Dry: Powdered reagents are injected, and the resulting salts are filtered out.
- Semi-dry: Reagents are sprayed as a slurry, reacting with acid gases before being captured as dry residues.
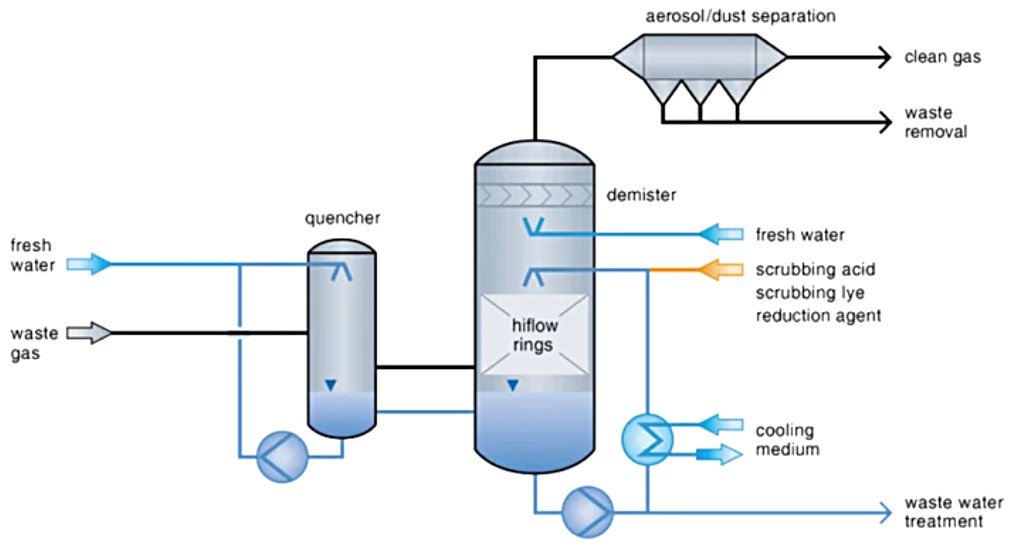
- Wet: Scrubbing with liquid absorbents (water or alkaline solutions) in scrubber columns removes acid gases, often with heat recovery (Fig. 1).
Figure 1 - Waste gas scrubbing | Basic stages[4]
3. Heavy Metals, Dioxins, and Organic Pollutants
4. Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) Reduction
- NOx is reduced by selective non-catalytic reduction (SNCR) or selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems, which convert NOx to harmless nitrogen and water using ammonia or urea as a reducing agent.
5. Final Polishing and Heat Recovery
- Additional steps may include flue gas condensation for heat recovery, polishing filters, or further scrubbing to ensure compliance with ultra-low emission limits.
Key Features
- Modular and Adaptable: Systems can be tailored with combinations of the above technologies to meet plant-specific requirements and local emission regulations.
- Multi-Pollutant Control: Modern flue gas cleaning often targets several pollutants in a single integrated system.
- Residue Handling: Byproducts such as neutralized salts, fly ash, and spent carbon are collected for safe disposal or further processing.
Typical Applications
- Biomass and waste-fired heat and power plants.
- Fossil fuel power stations.
- Industrial boilers and incinerators.
Summary
Flue gas cleaning is a multi-stage, adaptable process that ensures industrial exhaust gases are treated to remove dust, acid gases, NOx, and trace organic and metallic pollutants. It employs a combination of physical separation, chemical neutralization, and catalytic conversion, ensuring compliance with strict environmental standards and often enabling energy recovery from the cleaned gases
References
- Host Bioenergy > Technology > Flue gas cleaning. (Accessed 27th Jun 2025)
- Ruichang, 15th Apr 2023, Challenges and Opportunities for the Future of Flue Gas Cleaning Technology.
- Termomeccanica Ecologia > Flue Gas Treatment. (Accessed 27th Jun 2025)
- Hansa Engineering > Knowledge base > How does flue gas cleaning work? Key process parameters. (Accessed 27th Jun 2025)
- Harald Schrammel & Christian Ramerstorfer, Interreg Central Europe ENTRAIN, TT3: Emissions, Air Quality, Fuel and Ash Logistic Webinar, 2nd Dec 2020, Basics of flue gas cleaning.
- SODIMATE > What is Flue Gas Treatment? (Accessed 27th Jun 2025)
- Kanadevia Inova Steinmüller, SteinMûller Babcock Environment (Nippon Steel & Sumikin Engineering Group) Flue Gas Cleaning Brochure. (Document date: 18th Mar 2015)