Waste-to-Energy Plants
Incinerators are also called Waste-to-Energy (WtE) plants, or Energy-from-Waste plants (EfW).
Incineration Technologies
Incineration is the oldest technology used to process waste, consisting of several types of incinerators such as:
- Grate Incinerators
- Fluidized Bed Technologies
- Rotary Kiln Incinerators
They all involve directly combusting the MSW in an Oxygen-rich environment, typically at temperatures between 700°C and 1,350°C. An exhaust gas composed primarily of CO2 and water is produced, which flows through a boiler to produce steam to drive a steam turbine generator, producing electricity. Inorganic materials in the MSW are converted to bottom ash and fly ash. These by-products must be disposed in controlled and well-operated landfills to prevent ground and surface water pollution. Although incineration does not eliminate the need for landfills, it does significantly reduce the amount being sent to landfills by about 90% by volume.[1]
Rotary Kiln Incinerators
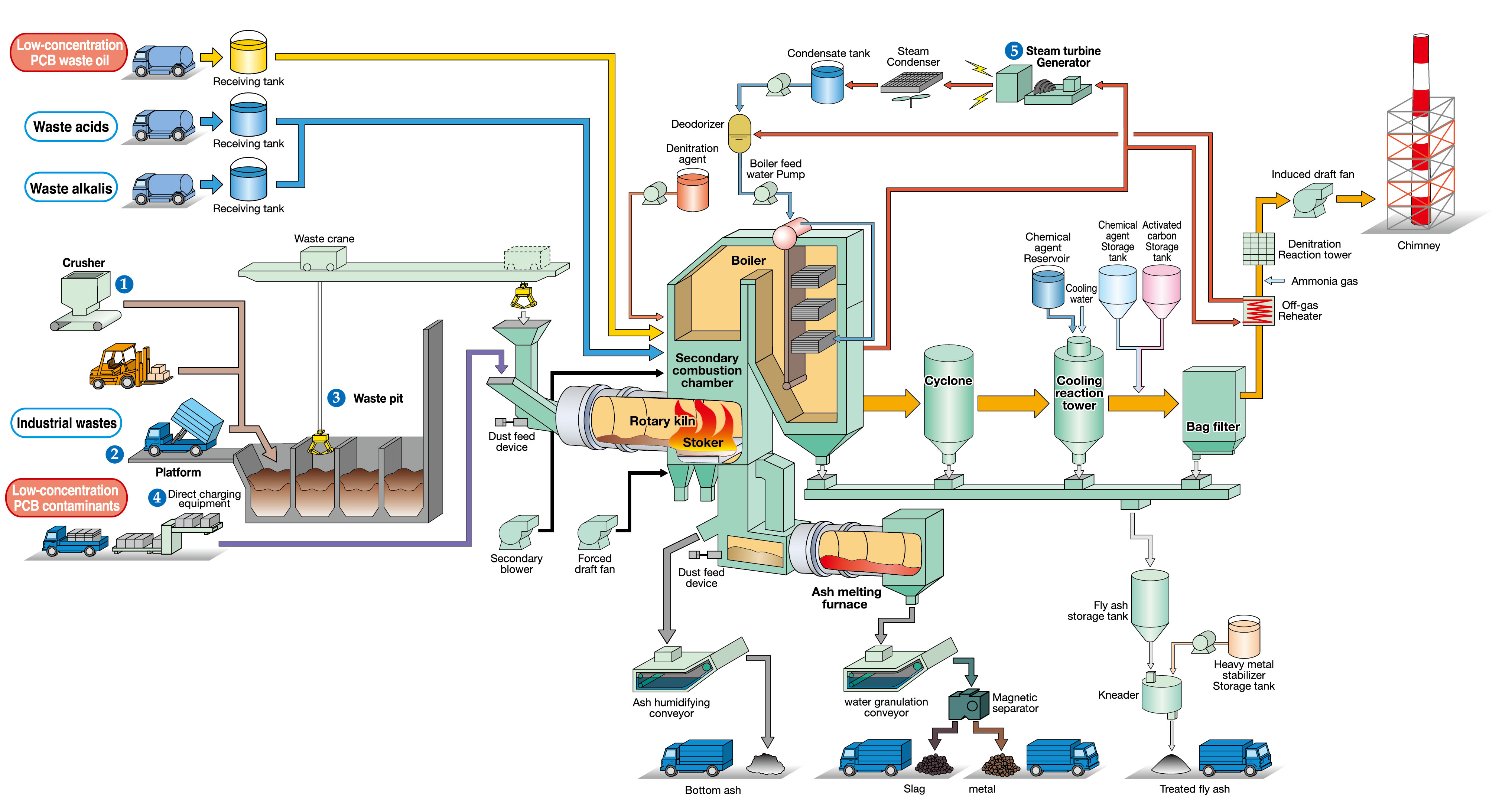
Rotary kiln incineration is a two-stage process employed essentially for treating hazardous medical, biological and industrial waste, waste material in a drum can, waste material contaminated with trace amounts of PCB. Temperatures of more than 1,100°C allow to control full destruction of organic compounds, viruses and microbes, low oxygen intake guarantees low emission values.
Companies such as Mitsubishi, Steinmueller and Babcock, or Sumitomo Heavy Industries are promoting the rotary kiln stoker for various kind of industrial waste. Pre-gasification occurs in the rotary kiln where easy-ignition waste such as high calorific waste is gradually incinerated under low-oxygen conditions. The residue dropping from the kiln is post-combusted in the stoker where hard-ignition waste is completely combusted with the formation of pyrolysis gas that undergoes secondary combustion when rising in the in the furnace[2].
Figure 3 - Rotary Kiln Incinerator Schematics.

Comparison of Incineration Technologies
Gasification and Rotary Kiln reactors have comparatively smaller waste treatment capacities reaching in the upper 10 tonnes per hour, or a maximum of about 80,000 tonnes per year[3],[4] compared with stoker type incinerators as shown in Table 1[3].
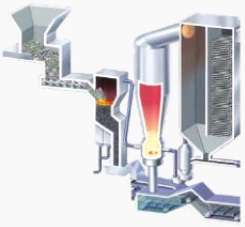
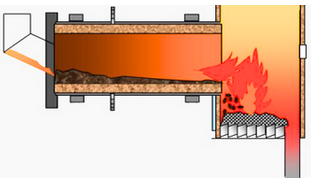
Table 1 - Comparison of different types of Mitsubishi incinerator technologies[3].
| Incinerator Type |
Stoker |
Gasification &
Ash Melting |
Rotary Kiln Stoker |
| Schematics |
 |
 |
 |
| Capacity per Unit |
100-1,000
tonnes per day |
100-200
tonnes per day |
100-250
tonnes per day |
| Waste Type |
MSW
Industrial Waste Biomass |
MSW |
Industrial waste |
| Advantages |
Construction costs
Waste flexibility
Proven records |
Recycling of
valuable metals
and slag |
Wide range
of waste types
is acceptable |
| Disadvantages |
Ash generation |
Construction costs |
Industrial waste only
(higher Lower Heating Value) |
References
- Adapted from: Yuzhong Tan, 15th Apr 2013, College of Engineering, University of California, Berkeley: Feasibility Study on Solid Waste to Energy - Technological Aspects.
- Yang, S., Kong, Q., Zeng, D. et al., Simulation research of a counter-flow rotary kiln hazardous waste incineration system, Int J Coal Sci Technol 9, 60 (2022).
- MHIEC Company and Waste to Energy Technology.
- NIPPON STEEL & SUMIKIN ENGINEERING Group’s Waste to Energy System.