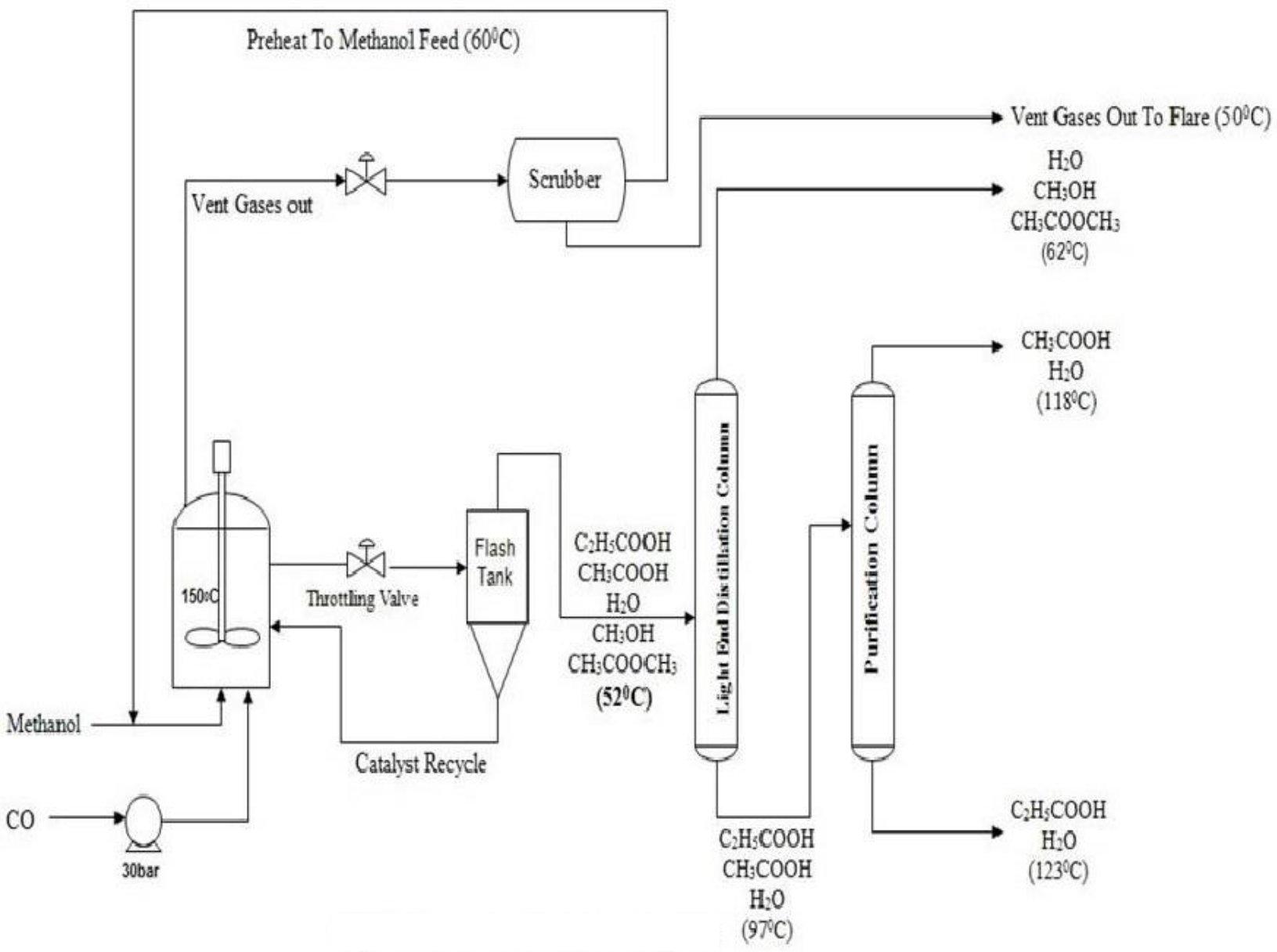
Reactions
The Main Reaction in the Methanol Carbonylation Process is the Insertion of Carbon Monoxide (CO) into the Methanol Molecule to form Acetic Acid[1]:
CH3OH + CO → CH3COOH ΔH = -138kJ/mol
Other Reactions involved are[1],[2]:
- the formation of Propionic Acid involving Ethanol as an Impurity in Methanol reacting with Carbon Monoxide:
C2H5OH + CO → C2H5COOH
- the formation of Methyl Acetate by Esterification of Acetic Acid with Methanol
CH3COOH + CH3OH → CH3COOCH3 + H20
- and the Water-Gas Shift Reaction, whereby Water reacts with Carbon Monoxide to form Carbon Dioxide and Hydrogen:
H2O + CO → C02 + H2
Processes
Production of Acetic acid by Carbonylation of Methanol used to be done by a Process named as Monsanto Process where Rhodium Catalyst was used as an Active Catalyst with Iodide of Metals such as Lithium. The Process was carried at 50-60 bar pressure and at a temperature of 150 to 200°C giving a high selectivity of 99% based on the Methanol Feed.
But BP Chemicals came up with a process named as Cativa that used Iridium Catalyst with Hydrogen Iodide as the Active Catalyst in the System. The first Methanol Carbonylation Pilot Plant was developed as early as 1925 by British Celanese. However, a lack of practical Materials that could contain the corrosive Reaction Mixture at the high pressures needed (200 atm or more) discouraged commercialization of these routes.
The first commercial Methanol Carbonylation Process, which used a Cobalt Catalyst, was developed by German Chemical Company BASF in 1963. In 1968, a Rhodium-based Catalyst (cis−[Rh(CO)2I2]−) was discovered that could operate efficiently at lower pressure with almost no By-Products. The first Plant using this Catalyst was built by US Chemical Company Monsanto in 1970, and Rhodium-catalyzed Methanol Carbonylation became the dominant Method of Acetic Acid Production.
In the late 1990s, the Chemicals Company BP Chemicals commercialized the Cativa Catalyst ([Ir(CO)2I2]−), which is promoted by Ruthenium. This Iridium-catalyzed Process has now largely supplanted the Monsanto Process, often in the same Production Plants.[1]