Process History
Borceed™ is a proprietary Borealis solution polymerisation technology[1], which is the rebranding of the DSM's Compact solution technology[2], which BOREALIS acquired from DSM in March 2013[3].
This solution polymerisation technology was developed in the 1960’s by the Stamicarbon subsidiary of DSM (Dutch State Mines). In 1972, DSM opened a solution PE plant in the Netherlands focused on Medium Density Polyethylene (MDPE) and High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) products. In 1981, the plant capability was extended to include Linear Low Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) and C8-based Polyolefin Plastomers (POP)[4,5].
The technology was operated from 1996 to 2013 by DEXPlastomers operating a plant with 120,000 tonnes/year solution PE capacity and using single site and solution process technologies to produce Exact metallocene-based plastomers and Stamylex linear polyethylene product families. Borealis announced in May 2013 that it will rename the Exact plastomers product range, calling it Queo™ polyolefin plastomers[2,6].
The proprietary solution process, referred to as the COMPACT technology, has been licensed worldwide by DSM[5,7]. Today, BOREALIS appears to be licensing out the Borceed™ technology as it is inviting companies interested in the technology to contact its innovation experts[1].
Process Operation
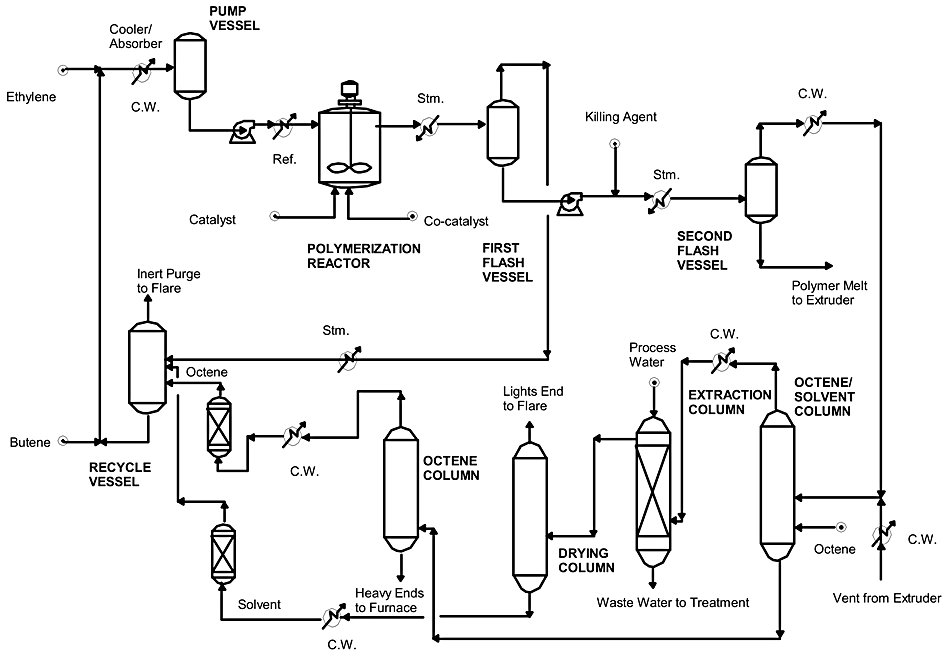
The plant is operated according to[7]:
- Polymer grade ethylene and the required comonomer are absorbed in the solvent (typically hexane) and the feed is refrigerated by heat of absorption in the cooler/absorber.
- From the cooler/absorber, the monomer-comonomer solution is fed to the reactor.
- Catalyst and co-catalyst are fed separately to the reactor.
- The polymerization is carried out in a single, agitated, completely liquid-filled vessel under adiabatic conditions.
- The heat of reaction is absorbed by the pre-cooled reactor feed.
- The reactor operates at temperatures between 150 and 250°C (302 and 482°F) and pressure between 30 and 100 bar (450 and 1400 psi).
- The residence time is less than 10 minutes, making grade changes very easy.
- Ethylene conversion per pass is 92-96 percent.
- Ethylene efficiency is over 99.5 percent for all grades.
- The heat of reaction is used to flash off the unconverted ethylene and the majority of the solvent and unconverted comonomer. The flash heater is able to flash up to 85 percent of the solvent in the reactor outlet stream.
- The overhead gas from the first flash vessel is condensed and recycled to the recycle vessel without any purification. A small purge stream from the recycle vessel prevents inerts from building up.
- The heat of condensation is used to generate low-pressure steam, which is used in the solvent recovery section.
- The solution is heated and fed to a second flash vessel (falling tower devolatilizer) in order to lower the volatile content to the required level.
- The final solvent removal is achieved in a vented extruder.
- The required additives are mixed with the molten polymer in the twin screw extruder before pelletizing. The polymer is pelletized under water and subsequently dried in a pneumatic impact dryer (low energy consumption) before pneumatic transport to blending and storage.
- The solvent recovered from the second flash vessel and extruder must be purified before being recycled to the reactor. This is accomplished in the solvent recovery section, which consists of distillation and extraction columns.
- In the first distillation column, the unconverted octene is separated from the solvent. Fresh octene is also fed to this column.
- The solvent (overhead) is sent to an extraction column to remove excess catalyst deactivator.
- The bottoms of the extraction column are sent to waste water treatment.
- The solvent leaves at the top of the column and is sent to a drying column for water removal. Although the water content of the solvent leaving this column is sufficient for the process, the liquid is sent through a molecular sieve as an added precaution before being recycled to the process.
- The bottoms stream from the first distillation column (octene-1), is sent to the second distillation column to separate the high boiling components from the octene comonomer.
- This octene stream is also put through a molecular sieve dryer before being recycled to the process.
References
- BOREALIS, Borceed™ Technology (accessed 27th May 2023).
- BOREALIS, Media Release, 7th Jun 2016, Borealis extends Queo™ plastomers portfolio with polyolefin elastomers, rebrands Compact technology to Borceed™.
- DSM, News, 4th Mar 2013, DSM completes sale of participation in DEXPlastomers JV to Borealis.
- megr, M&A Deal Summary, 1st Jan 1996, DSM Plastomers B.V. and Exxonmobil Chemical Holland B.V. Acquire DEXPlastomers V.o.F.
- Burdett, Ian & Eisinger, Ronald. (2016). Ethylene Polymerization Processes and Manufacture of Polyethylene. 10.1002/9781119159797.ch3.
- PLASTICS TODAY, 5th Jun2013, New Borealis plastomers unit enters growing market with new name, range.
- Nexant Chem Systems, PolyOlefin Planning Service 2001, Report 2: Global Commercial Analysis and Technology Review, Part B: Technology Review.