Technology History and Ownership
Origins and Development (1980s–1995)
Spherilene is a gas-phase polyethylene process developed by Himont Italia (a member of the Montedison group) at the G. Natta Research Center in Ferrara, Italy, during the late 1980s and early 1990s. The technology was specifically designed to combine low-cost gas-phase operation with exceptional product flexibility, addressing the traditional limitation where different PE processes were required for different grades (slurry for HDPE, solution for LLDPE/VLDPE, gas-phase for commodities).
The process was first publicly described in technical literature in 1995 by Massimo Covezzi of Himont Italia. Spherilene became the first industrialized polyethylene gas-phase technology featuring two gas-phase reactors in series—a groundbreaking configuration that enabled production of reactor-blend bimodal products.
Corporate Succession and Ownership
The Spherilene technology ownership followed this path:
- 1980s–1993: Developed by Himont (Montedison/Hercules joint venture)
- 1995: Held by Montell Polyolefins (Shell/Montedison joint venture formed 1995), which merged Himont's polyolefin assets with Shell's operations
- 2000: Transferred to Basell through the three-way merger of Montell (Shell/Montedison, holding Spherilene), Elenac (BASF/Shell, holding Lupotech G), and Targor (BASF/Hoechst)
- 2007–present: Owned by LyondellBasell following the Basell–Lyondell merger
Relationship with Lupotech G
When Basell was formed in 2000, it inherited both Spherilene (from Montell/Himont) and Lupotech G (from BASF/Elenac) as competing gas-phase PE technologies. Basell's initial licensing strategy maintained both brands, but:
- Spherilene was actively promoted globally for new licenses (especially the Spherilene S single-reactor variant)
- Lupotech G was retained for legacy in-house plants but licensing was phased out by ~2010
Current Licensing Position
LyondellBasell has discontinued licensing of Spherilene technology and no longer builds new Spherilene-based plants. The technology has been effectively superseded by LyondellBasell's Hyperzone PE process, which represents a strategic consolidation and evolution of the company's PE technology portfolio.
Process Description and Operating Conditions
Core Process Features
Reactor Type: Gas-phase fluidized-bed polymerization
Catalyst System:
- Spherical morphology catalysts supported on activated MgCl₂
- Two primary catalyst families:
- Catalyst 201: Broad MWD HDPE catalyst (chromium-based)
- Catalyst 202: Narrow MWD HP-LLDPE catalyst (Ziegler-Natta titanium-based)
- Avant Z-series Ziegler-Natta catalysts for modern installations
- Chromium catalysts for specialty HDPE/MDPE grades
- Complete compatibility between HDPE and LLDPE/VLDPE catalyst families
Key Innovation: Spherical-form polymer particles (1,000–3,000 micron diameter) produced directly in the reactor, enabling pelletization-free commercialization for many grades.
Process Flow
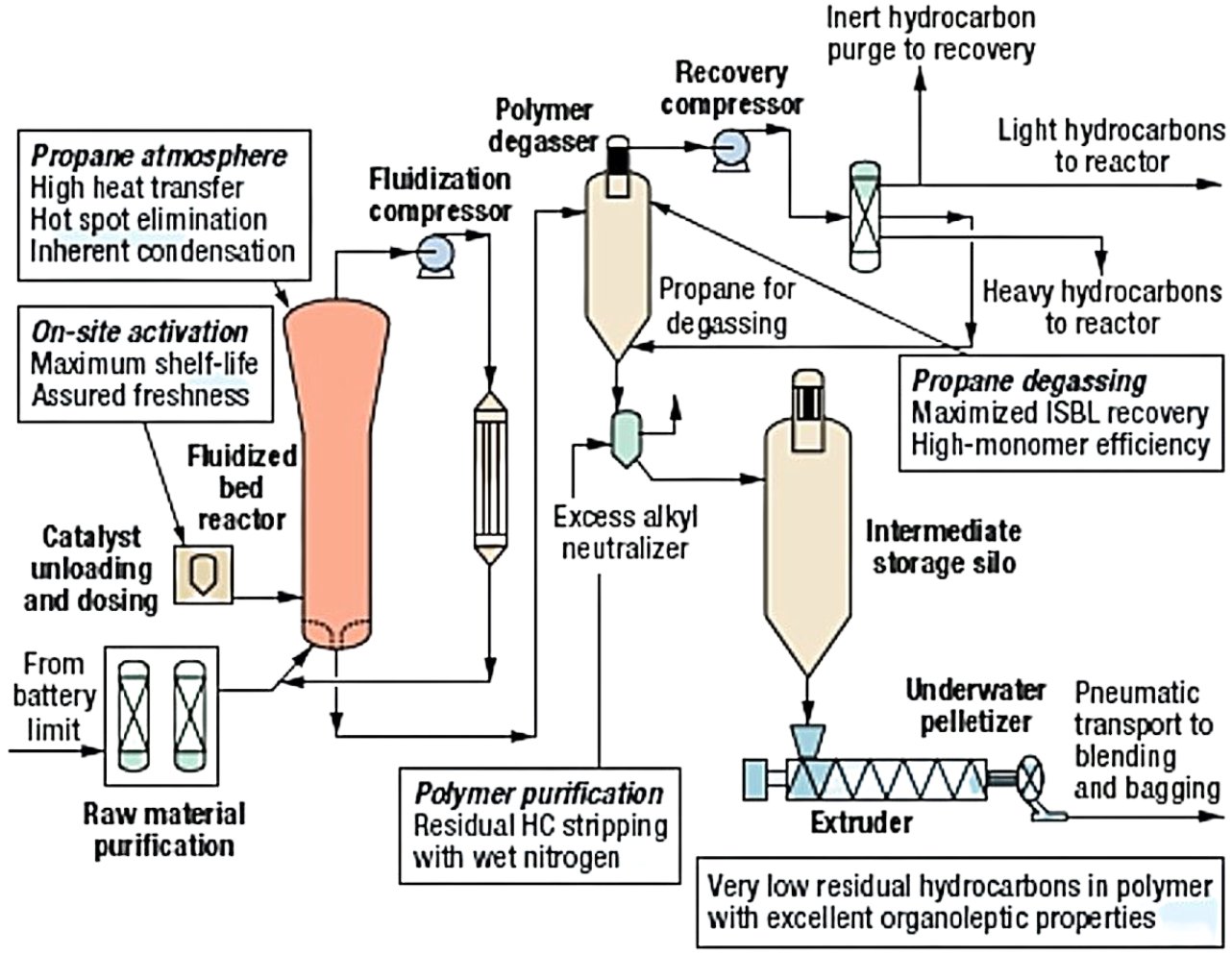
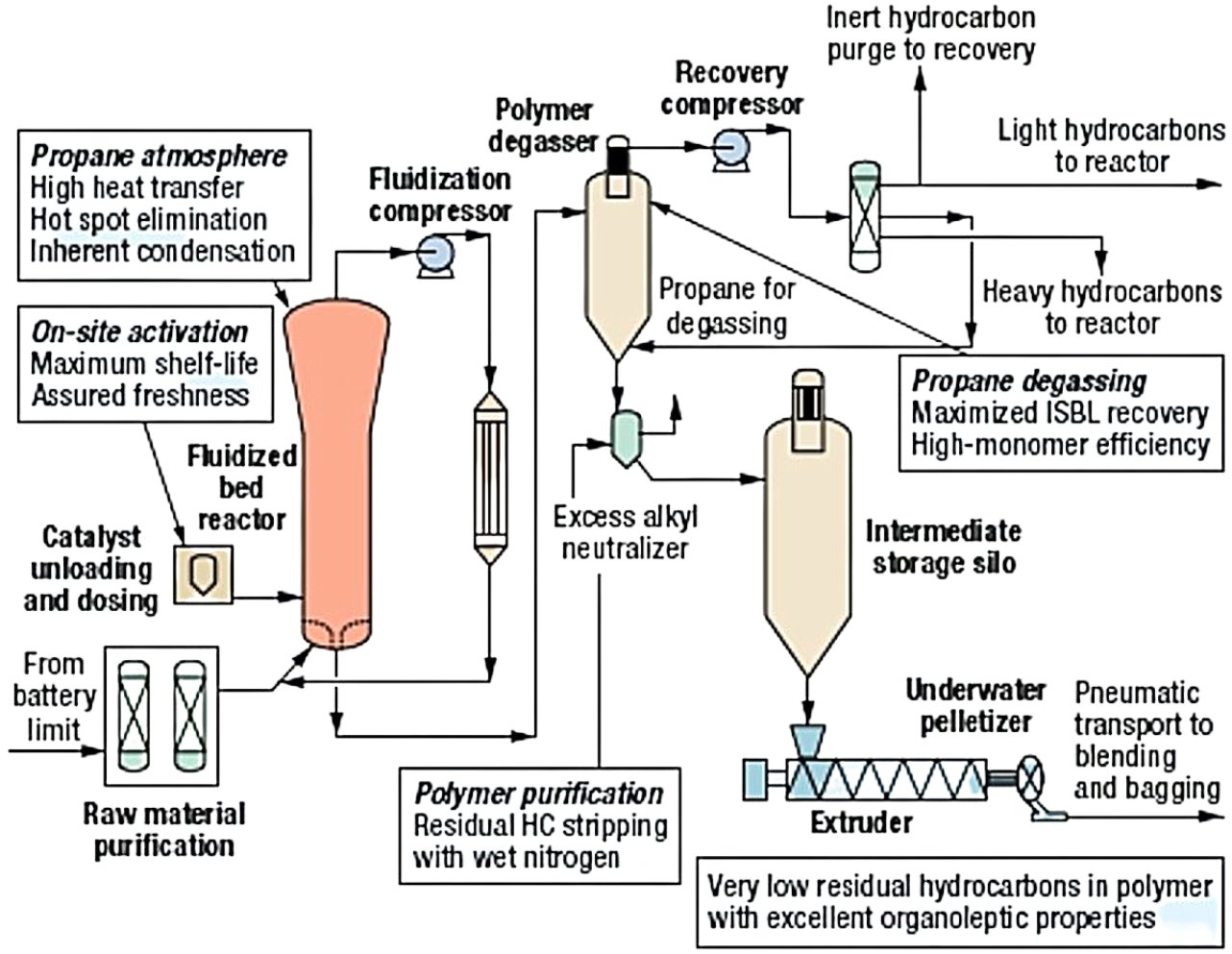
Simplified Spherilene Process Flow Diagram
- Catalyst Preparation:
- Solid catalyst, alkyls and donor are brought into contact in the pre-contact vessels, where the catalyst is activated; activated catalyst stream from the pre-contact vessel flows directly into the gas phase reactor and is dispersed in the fluidized reacting bed.
- The spherical morphology Avant Z catalysts can be introduced directly into the reactor, even when empty.
- Chromium or other specialty catalysts are introduced when there is a seed bed in the reactor.
- Gas-Phase Polymerization:
- Ethylene, comonomer (propylene, butene, hexene), and hydrogen are fed to the reactor according to the required production capacity and proportions needed for the target product.
- Propane is used as the inert medium of reaction and provides an independent means of controlling the reaction kinetics while providing a heat removal capability far superior to that of inorganic inerts (such as nitrogen).
- The heat of the reaction is removed from the fluidizing gas in a water cooled vertical heat exchanger.
- Operating conditions:
- Pressure: 15–30 bar (typical gas-phase range)
- Temperature: 70–110°C (catalyst-dependent)
- Residence time is 2.5 hours in the polymerization section
- The polymer is withdrawn continuously from a specially designed outlet at the bottom of the reactor
- Downstream Processing
- Polymer withdrawn from the reactor is sent to a degassing vessel where monomer unreacted, comonomer and hydrogen are removed from the polymer with the help of a counter-current propane gas flow
- Deassed polymer is fed by gravity to a deactivation vessel where the dissolved hydrocarbons are removed from the polymer by counter-current stripping with nitrogen assisted by a small amount of steam; steam also ensures that any residual activity of catalyst system components is neutralized completely
- From the bottom of the deactivation vessel, the polymer is conveyed pneumatically to the powder silo located on top of the extruder
- The silo is provided with nitrogen purging to ensure that no residual hydrocarbons accumulate in the silo
- Polymer from the silos is mixed with required additives before being fed to the extruder
- Residence time in finishing section is 20 minutes
- Final polymer has zero monomer residue and chlorine below 50 ppm
- Monomer Recovery:
- The recovered gas is sent to the hydrocarbon recovery section, where the reaction components are separated from propane
- Both fractions are recycled inside battery limits as appropriate.
Dual-Reactor Configuration (Spherilene's Signature Feature)
Spherilene is the first PE gas-phase technology industrialized with two gas-phase reactors in series. Key aspects:
- Lock-hopper system between reactors provides complete gas separation between stages
- Enables synthesis of different polymer structures in each reactor (bimodal "reactor blends")
- First reactor produces base polymer (e.g., HDPE backbone); second reactor adds copolymer phase (e.g., LLDPE tie layer)
- Single-reactor plants can be retrofitted with a second reactor to increase capacity and expand product capability
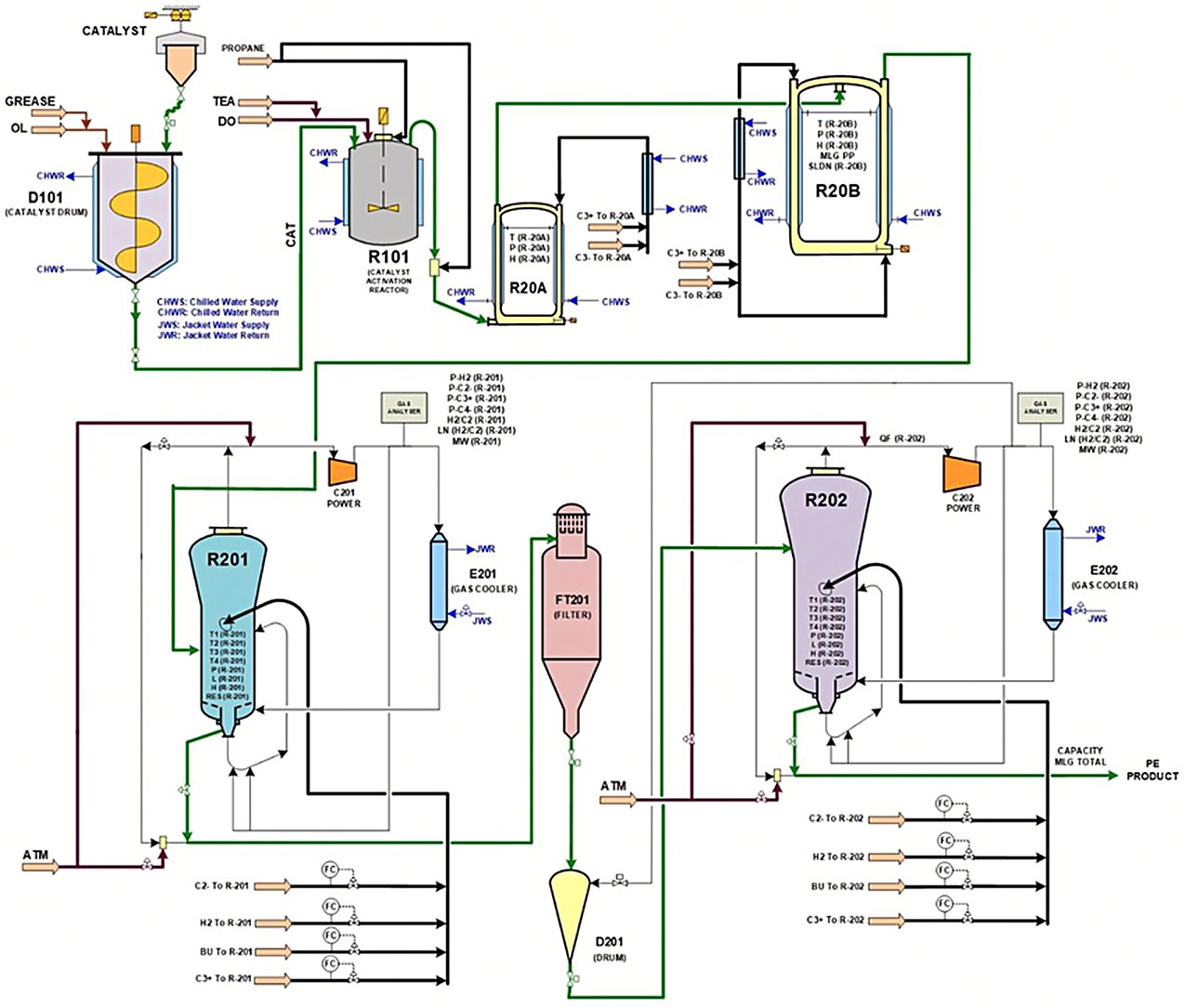
Process flow diagram of Spherilene technology with Dual Gas Phase Reactors and process variables (ATM, atmer; DO, donor; TEA, teal.
Product Range and Performance
Density and Melt Index Range
- Density: 0.890–0.970 g/cm³ (full VLDPE to HDPE spectrum)
- Melt Index: 0.01–100 g/10 min (2.16 kg)
- Melt Flow Ratio: 25–120 (one-step); 80+ (two-step bimodal)
Product Grades
| Grade Type |
Density (g/cm³) |
Applications |
Catalyst |
| HDPE |
0.940–0.965 |
Blow molding, pipe, sheet,
film, injection molding |
Catalyst 201 (Cr) |
| MDPE |
0.930–0.940 |
Pipe,
rotational molding |
Catalyst 201 (Cr) |
| LLDPE |
0.910–0.930 |
Film, sheet,
injection molding |
Catalyst 202 (ZN) |
VLDPE /
HP-LLDPE |
0.890–0.910 |
High-performance film,
blending |
Catalyst 202 (ZN) |
HP-LLDPE (High-Processability, High-Performance LLDPE)
A breakthrough grade family introduced by Spherilene, designed to overcome conventional LLDPE's processing limitations:
- Processability similar to LLDPE/LDPE blends (15–25% LDPE equivalent)
- Mechanical properties equal or superior to C6/C8 LLDPE
- Superior bubble stability in blown film
- Lower energy consumption (measured amperage and kWh/kg) compared to conventional LLDPE or LLDPE/LDPE blends
- Excellent optical properties (haze, gloss)
- Raw materials cost equal to butene LLDPE (no need for expensive HAO comonomers or LDPE blending)
Economics and Environmental Performance
Investment and Operating Costs
From the 1995 Himont paper:
| Cost Category |
Spherilene
Index |
Spherilene
(no extrusion) |
Competitor A |
Competitor B |
| Investment |
88 |
75 |
100 |
95 |
| Materials |
100 |
100 |
101 |
105 |
| Utilities |
100 |
100 |
108 |
103 |
Spherilene without extrusion offers 25% lower investment and marginally lower utilities compared to benchmarked technologies.
Raw Materials and Utilities (per tonne PE, single reactor)
- Ethylene + comonomer: 1,010 kg/t product
- Low-pressure steam: 200 kg/t
- Cooling water: 120 m³/t
- Power (no extrusion): 190 kWh/t
Environmental Footprint
- Liquid emission: 0.5 t/t polymer (condensed process steam)
- BOD: 100 mg/L; COD: 200 mg/L
- Zero monomer residue in final polymer
- Complete recovery and recycling of heavy comonomers
Commercial Experience
Spherilene Technology: Current Global Installed Capacity Summary:
| Plant |
Location |
Capacity (kt/y) |
Status |
Notes |
| Lorestan Petrochemical |
Iran |
300 |
Operating |
Project startup
delayed but
marked completed |
| Mahabad Petrochemical |
Iran |
300 |
Operating |
Production increased
to 320 kt/y in 2019 |
| Haldia Petrochemicals |
India |
386 |
Operating |
3rd Spherilene plant worldwide |
Braskem
Triunfo |
Brazil |
333 |
Operating |
Expanded
2025 |
| JG Summit |
Philippines |
570
(total PE) |
Shut down 2025 |
Indefinite closure |
| Total Active |
— |
~1.350 |
— |
Excluding
JG Summit |
References
- Jack. Jun 17, 2018. LL/MD/HDPE Process by LyondellBasell. Oil & Gas Process Engineering
- M. Covezzi. 1995. The Spherilene process: Linear polyethylenes. Macromolecular Symposia. 89(1), pp. 577–586. DOI: 10.1002/masy.19950890153, and references cited therein
- Wikipedia. (Last edited: Mar 1, 2025). Basell Polyolefins
- Dec 23, 1997. Case No IV/M. 1041 - BASF / SHELL. Commission of the European Communities
- Mar 29, 2000. Case No COMP/M.1751 - SHELL / BASF / JV - PROJECT NICOLE. Commission of the European Communities
- M. Covezzi et al. European Patent EP0560312B1: Process for the gas-phase polymerisation of olefins. Mar 10, 1993: Application filed by Montell Technology Co BV
- M. Covezzi et al. United States Patent US5733987A: Process for the gas-phase polymerisation of olefins. Mar 12, 1993: Application filed by Montell Technology Co BV
- LyondellBasell Industries. Licensing & services - Technologies. Retrieved Dec 9, 2025
- A. Tullo. Aug 8, 2016. LyondellBasell plant to debut polymer process. Chemical & Engineering News, 94 (32), pp. 12-13
- F. Jani et al. 2024. Enhancing quality control of polyethylene in industrial polymerization plants through predictive multivariate data‐driven soft sensors. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering. 103. 2234-2250. DOI: 10.1002/cjce.25479.
- Oct 24, 2005. Iran selects Basell's Spherilene technology for new LLDPE plant. plastemart
- Lorestan LLDPE/HDPE project status: Completed. IranOilGas Network
- Mahabad LLDPE/HDPE project status: Completed. IranOilGas Network
- E. Baghishov. Apr 1, 2019. Production of Iran's Mahabad Petrochemical Complex up by 20%. Trend News Agency