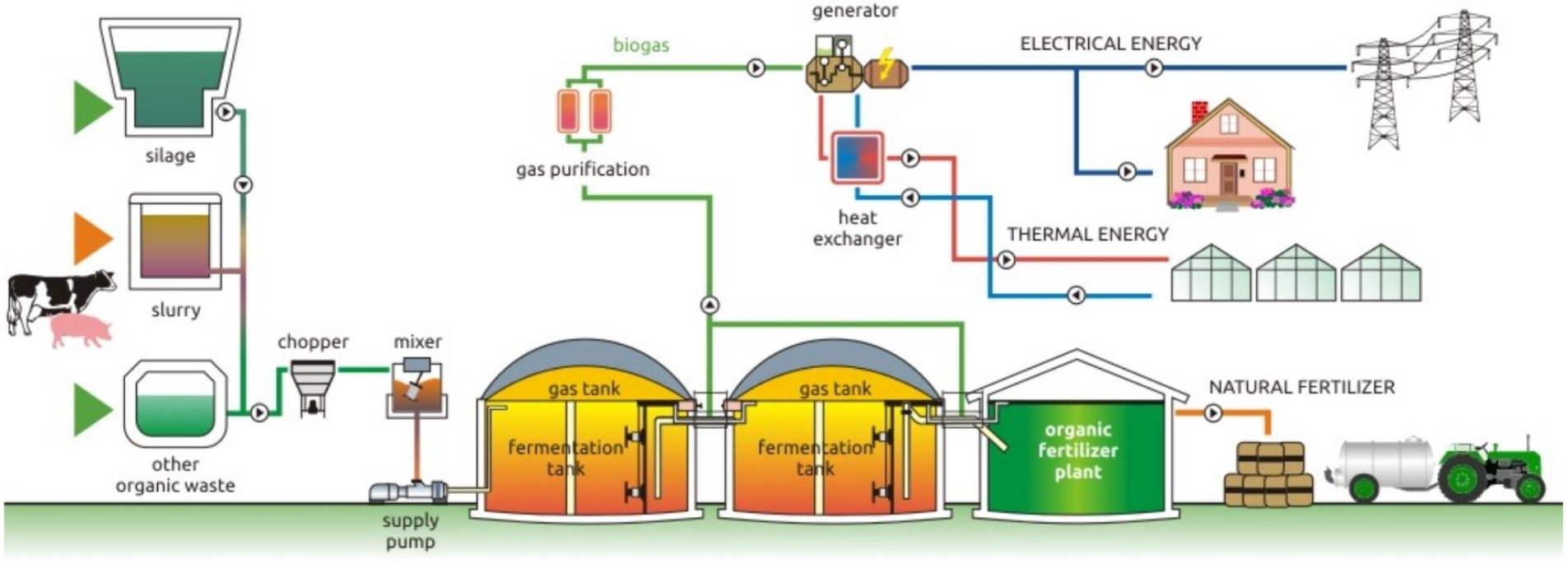
While some steps could vary with each biogas plant, most facilities use the same process to produce biogas.
Step 1 – Pre-treatment and filling the digester
Multiple types of organic matter, called substrates, go into the digester. Some substrates can be liquid manure, renewable raw materials (such as corn or grass), or waste produced by the food industry. Some of them may need to be stored in cement containers and pre-treated before entering the air-tight tank. One plant can include several digesters, depending on its size.
Step 2 – The fermentation process
The substrates are heated to various temperatures inside the fermenter, and a series of microorganisms start breaking down the organic matter in the absence of light and oxygen. During the process, the organic matter is shifted to prevent layers from forming at the top and bottom of the tank.
Step 3 – Producing biogas
As a result of the fermentation, biogas with methane as the main ingredient is produced inside the fermenters. At this stage of the process, the gas includes, besides methane and carbon dioxide, water and hydrogen sulfide—which is one of the main reasons containers should be made in steel, known to withstand the effects of the gas for long periods.
Step 4 – Pulling out the residues
After fermentation, the residues called digestate are pulled out of the tank to be used as environment-friendly, high-quality fertilizer. This way, the biogas production process becomes a zero-waste system of eliminating garbage from landfills while providing a solution for better crops at the same time.
Step 5 – Eliminating impurities
The biogas goes through a cleanup process, in which water, hydrogen sulfide, and impurities are removed to produce biomethane that can further be used to generate energy and heat. The biogas is permanently monitored to ensure the quality of the final product.
Source: HOMEBIOGAS, WHAT IS A BIOGAS PLANT AND HOW DOES IT WORK?