Product
- Product
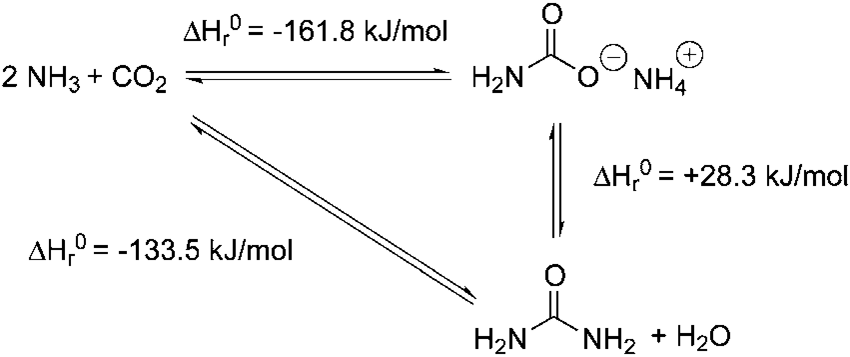
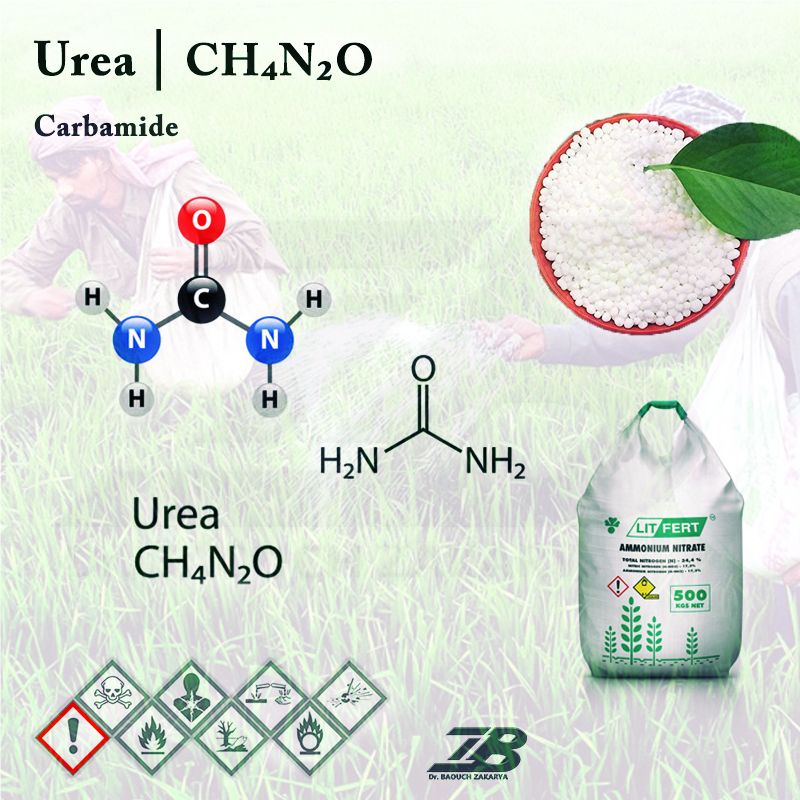
- Urea
- Names
- Carbamide; Carbonyldiamide; Carbonyldiamine; Diaminomethanal; Diaminomethanone
-

- #PS484
- Main Product
- Ureas
- Segment
- Chemicals
- Main-Family
- Functional Organic Products
- Sub-Family
- Amids & Lactams
- Physical State
-
Solid
Description
Your insights will be shown here
Product Communicator
| Title | Date | |
|---|---|---|

|
5/6/2023 |
Chemical Data
- Chemical Formula
-
CN2H4O
- Molecular Weight (g/mol)
- 60.06
- Melting Point (°C)
- 134
- Sulfur Content (wt%)
- 0
- Specific Gravity
- 1.32
Crude Data
- API Gravity
- -24.3
- Country
Product Settings
- Default
- Status
- A
Content provided by
| Transaction | Name | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Modified by |
|
9/5/2024 12:53 PM |
| Added by |
|
2/7/2023 8:09 AM |