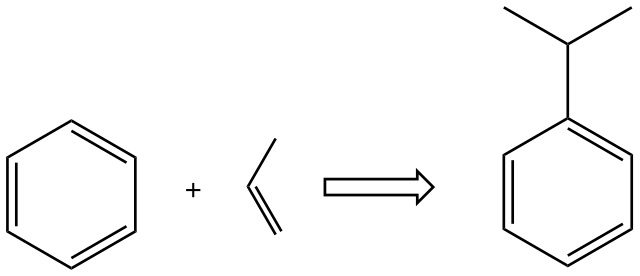
Product
- Product
- Cumene
- Names
- Isopropylbenzene; Cumol; (1-Methylethyl)benzene; (Propan-2-yl)benzene
-

- #PS3
- Main Product
- Propylbenzene
- Segment
- Chemicals
- Main-Family
- Aromatics
- Sub-Family
- Benzene & Homologues
- Physical State
-
Liquid
Description
Your insights will be shown here
Product Communicator
| Title | Date | |
|---|---|---|

|
10/25/2024 | |

|
9/23/2021 |
Identifiers
-
 CAS Number
CAS Number
- 98-82-8
-
 EC Number
EC Number
- 202-704-5
-
 ECHA InfoCard
ECHA InfoCard
- 100.002.458
-
 IUPAC Name
IUPAC Name
- (Propan-2-yl)benzene
-
 PubChem ID
PubChem ID
- 7406
Chemical Data
- Chemical Formula
-
C9H19
- Molecular Weight (g/mol)
- 120.195
- Boiling Point (°C)
- 152
- Melting Point (°C)
- -96
- Sulfur Content (wt%)
- 0
- Specific Gravity
- 0.87
Crude Data
- API Gravity
- 10
- Country
Product Settings
- Default
- Status
- A
Content provided by
| Transaction | Name | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Modified by |
|
7/3/2025 3:28 PM |
| Added by |
|
2/15/2021 11:48 AM |