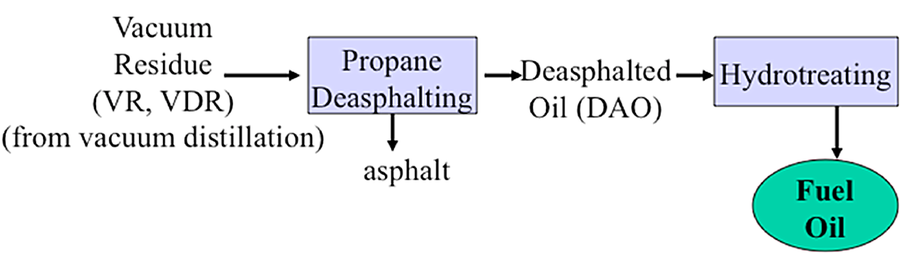
Product
- Product
- Petroleum Pitch
- Names
- Petroleum asphalt; Bitumen; Petroleum tar; Pitch, petroleum, arom.; PR (petroleum pitch); Aromatic petroleum pitch
-

- #PS248
- Main Product
- Pitch
- Segment
- Refined Products
- Main-Family
- Refinery Residues
- Sub-Family
- Coal & Petroleum Residues
- Physical State
-
Solid
Description
Your insights will be shown here
Product Communicator
| Title | Date | |
|---|---|---|

|
1/4/2025 | |

|
11/9/2021 |
Identifiers
-
 CAS Number
CAS Number
- 68187-58-6
-
 EC Number
EC Number
- 269-110-6
-
 ECHA InfoCard
ECHA InfoCard
- 100.062.808
Chemical Data
- Molecular Weight (g/mol)
- 516
- Specific Gravity
- 1.02
Crude Data
- API Gravity
- 7.91
- Country
Product Settings
- Default
- Status
- A
Content provided by
| Transaction | Name | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Modified by |
|
1/4/2025 10:06 AM |
| Added by |
|
11/9/2021 12:51 PM |