Lignite, also called brown coal, is the lowest-rank coal formed from peat at shallow depths and temperatures below 100°C (212°F). It is the first product of coalification, intermediate between peat and subbituminous coal, and appears brownish-black to dark brown in color.
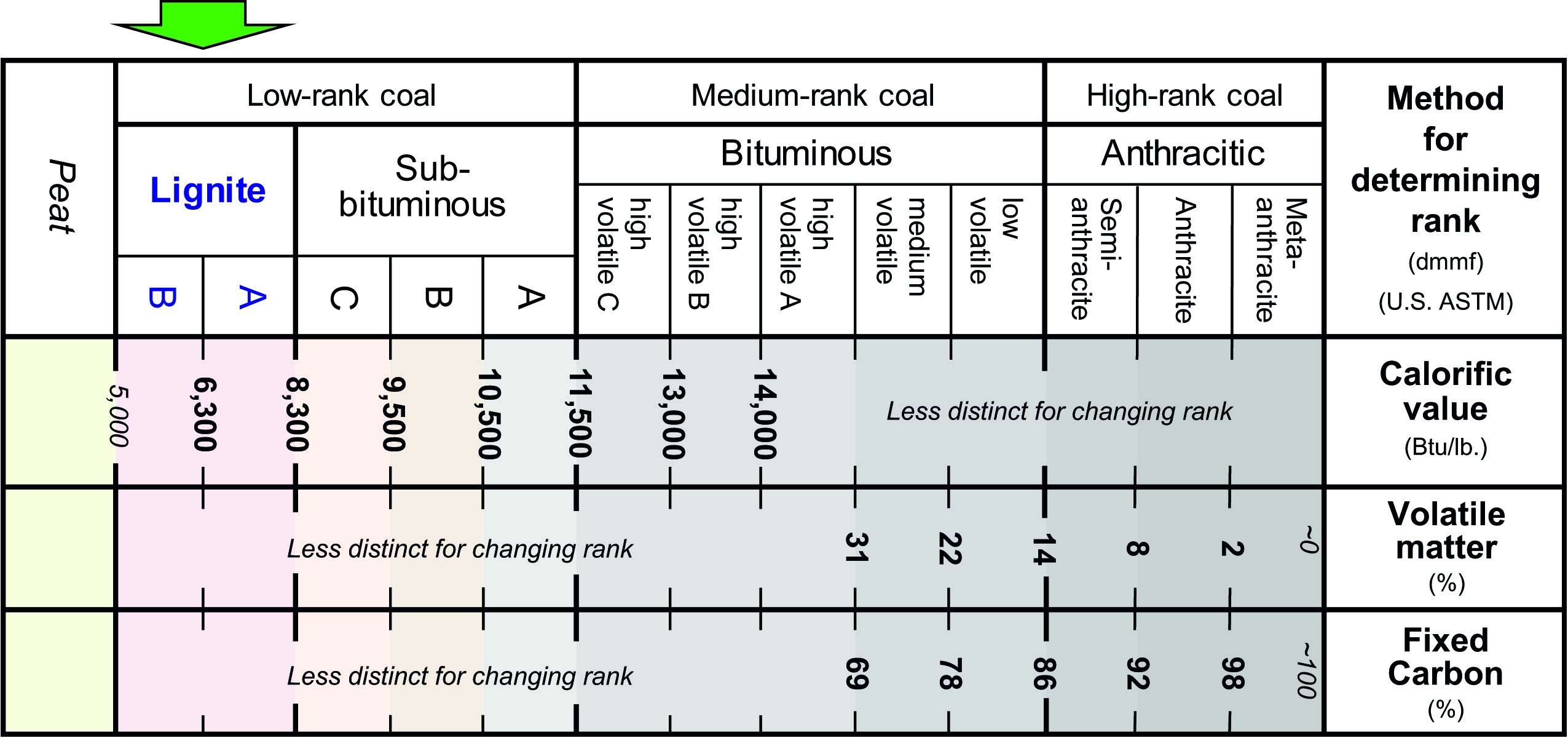
Lignite rank and defining characteristics [6]
Carbon and Moisture Content
Lignite contains 60-70% carbon on a dry, ash-free basis, but only 25-35% carbon on an as-received basis due to extremely high moisture content. The inherent moisture content ranges from 30-75%, with some deposits reaching 60-70%, which is the defining characteristic that distinguishes lignite from higher-rank coals. This high moisture dramatically reduces heating value and combustion efficiency while increasing CO₂ emissions per unit of energy output.
Physical and Chemical Properties
The coal has a calorific value of approximately 17 MJ/kg (4,000-4,600 kcal/kg), significantly lower than higher-rank coals. Ash content ranges from 6-19%, and volatile matter is very high at 45-55% on a moisture and ash-free basis, making lignite easier to gasify and liquefy than higher-rank coals. The coal is soft and friable with a Hardgrove Grindability Index around 100, making it easy to pulverize but also susceptible to spontaneous combustion during storage.
Characteristics and Formation
Lignite is non-caking and non-coking, meaning it does not form hard clumps or agglomerate when heated. The coal often retains visible woody cellular structure from original plant material, indicating its geologically young age. Sulfur content is typically low, though ferrous sulfide presence can lower ash fusion temperatures to around 900°C, creating slagging potential. Because lignite deposits occur near the surface, they are economically mined by open-pit methods without the methane risks associated with underground mining.
References
- Wikipedia. Lignite (page version: Dec 27, 2025)
- Kopp O.C. (Dec 3, 2025). lignite. Britannica
- Satyendra (Aug 27, 2018). Lignite Coal. Ispat Guru
- Science Direct. Lignite
- Vedantu. Lignite: Characteristics and Uses in Chemistry (May 5, 2021)
- Kentucky Geological Survey, University of Kentucky. Lignite Coal
- Jay Ganesh Minerals. How Lignite Coal is Mined, Refined and Processed (Jul 3, 2025)
- Niyas (Dec 1, 2024). Lignite coal. GOODWIND
- Lignite Energy Council. What is Lignite? (Mar 5, 2024)