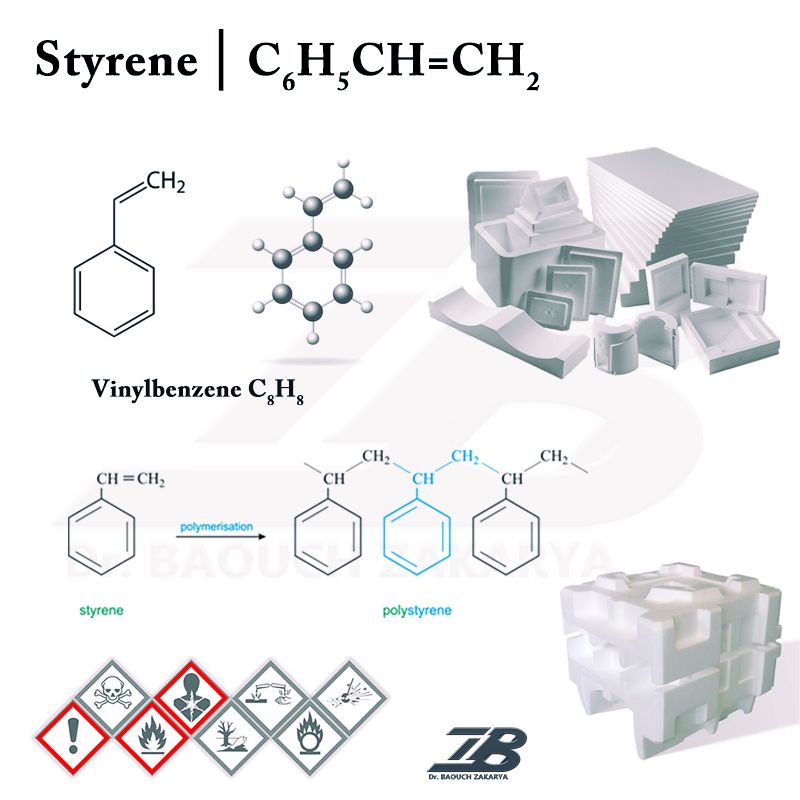
Styrene (C6H5CH=CH2; phenylethylene, vinylbenzene, styrene monomer) is the common name given to the simplest and most important member of the unsaturated aromatic monomers family, which is a colorless oily liquid.
It is a very important chemical, which is mostly used to produce polystyrene converted into daily-use plastic materials and items such as toys, jars, bottles, serving dishes, cups, corks, etc., as well as a foam precursor for insulation and cushioning operations.
Styrene is obtained at commercial scale through several production processes, among which the most important ones are:
-
Catalytic dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene at high temperature (630 °C) using various metal oxides as catalysts, such as zinc, chromium or magnesium oxides coated on activated carbon, alumina or bauxite.
-
Ethylbenzene oxidation to obtain the hydroperoxide, which then reacts with propylene to give phenylmethylcarbinol (or methylbenzylalcohol) and propylene oxide. The alcohol obtained is then dehydrated to styrene at relatively low temperatures (180 to 400 °C) by using an acidic silica gel (SiO2) or titanium dioxide (TiO2) catalyst.
Source: Amaury Pérez-Sánchez et al., 28th Apr 2017, Simulation of the styrene production process via catalytic dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene using CHEMCAD® process simulator, Tecnura, vol. 21, no. 53, pp. 15-31, 2017.