Main-Product
- Product
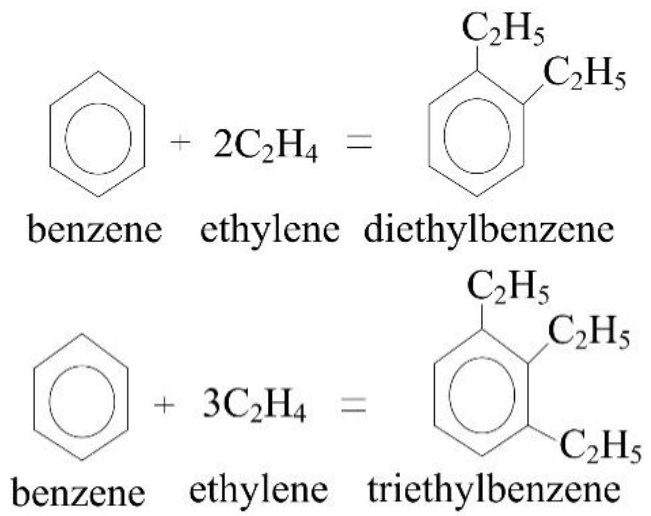
- Polyethylbenzene
- Segment
- Chemicals
- Main-Family
- Aromatics
- Sub-Family
- Benzene & Homologues
- Link
-

- #PS661
Description
Your insights will be shown here
Product Communicator
(*=Default)| Product | Title | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|

|
4/20/2025 | ||

|
4/20/2025 |
| Products (Quick Access) | Abbr. | Default |
|---|---|---|
| Polyethylbenzene | PEB | |
| Diethylbenzene | DEB |
Settings
- Status
- A
- Unit of Measure
- Metric Ton
- Physical State
-
Liquid
Building Block / Value Chain Info
Content provided by
| Transaction | Name | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Modified by |
|
4/20/2025 1:21 PM |
| Added | 4/20/2025 9:56 AM |