Combustion energy potential refers to the amount of chemical energy stored in a fuel that can be released through combustion. This potential is typically measured as the heat of combustion, also known as calorific value or energy value. It represents the total heat released when a specified amount of fuel undergoes complete combustion with oxygen under standard conditions.
Chemical Basis of Combustion Energy
Combustion is fundamentally a redox reaction between a fuel (reductant) and an oxidant that produces oxidized products while releasing energy. The process requires an initial activation energy to overcome the energy barrier, but once initiated, the reaction often becomes self-sustaining as the released energy enables further reactions.
For hydrocarbon fuels, the general combustion reaction follows this pattern:
Fuel + O2 → CO2 + H2O + Energy
The coefficients of the balanced equation will change depending on the fuel. The balanced equation for methane (natural gas) is:
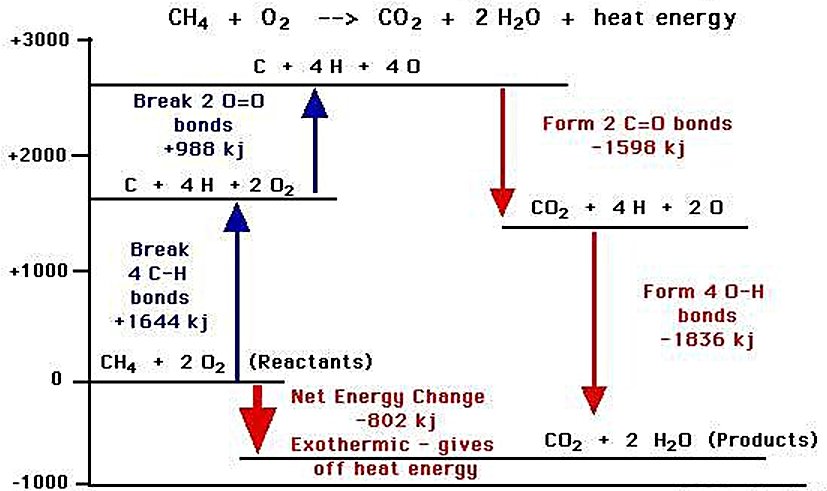
CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O + Energy
The energy potential of combustion is typically measured as the heat of combustion, also known as calorific value or energy value. This represents the total amount of heat liberated when a given amount of substance undergoes complete combustion with oxygen under standard conditions.
Comparative Combustion Energy Potential
The combustion energy potential varies significantly among different fuels:
Gaseous Fuels
Liquid Fuels
Solid Fuels
References
- Wikipedia, Heat of Combustion. (accessed 30th Mar 2025)
- Milczanowski, Combustion reactions, Florida State College at Jacksonville, retrieved via the Web Archive, Sep 2024.
 Kokel, Nicolas
Kokel, Nicolas