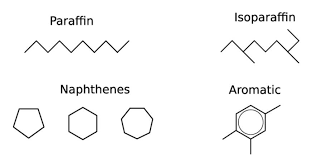
Paraffins are also called Alkanes and have the general formula of CnH2n+2, where n is the number of Carbon Atoms in a given Molecule. Paraffins are divided into two groups of normal- and iso-Paraffins.
Normal Paraffins or normal Alkanes are simply written as n-Paraffins or n-Alkanes, and they are open, straight-chain saturated Hydrocarbons. Under standard conditions of temperature and pressure (STP), the first four members of the Alkane series (Methane, Ethane, Propane, and Butane) are in gaseous form, and Compounds starting from C5H12 (Pentane) to n-Heptadecane (C17H36) are liquids (constituting large fractions of Hydrocarbons found in liquid Fuels (e.g., Gasoline, Jet Fuel, and Diesel Fuel), whereas n-Octadecane (C18H38) or heavier Compounds exist in isolation as Wax-like solids at STP.
Isoparaffins, which are branched-type Hydrocarbons, begin with Isobutane (also called Methylpropane), which has the same closed formula as n-Butane (C4H10). Branching in Hydrocarbons causes significant changes in physical properties (e.g., boiling point and density) and chemical behavior (e.g., Octane number) of Paraffins with the same Carbon number. A specific nomenclature using Alkyl Groups serves to specifically name Isoalkanes (e.g., 2,2,4-Trimethylpentane to designate a specific iso-Octane).
Naphthenes or Cycloalkanes are rings or cyclic saturated Hydrocarbons with a general formula of CnH2n. Cyclopentane (C5H10), Cyclohexane (C6H12) and their derivatives such as n-Alkylcyclopentanes are normally found in Crude Oils.
Source: FSC 432, Petroleum Processing, Paraffins, College of Earth and Mineral Sciences, Penn State.